Neptune Image List

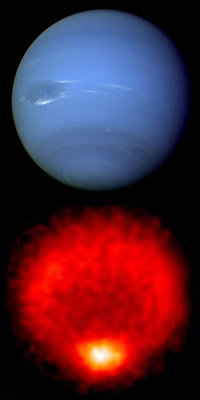
This is a color image of Neptune showing the Great Dark Spot. (Courtesy of NASA)
(32K JPG)

This is an image showing crescents of Neptune and its moon Triton taken by
Voyager 2 on August 31, 1989. (Courtesy of NASA)
(24K JPG)

This is a false color image of Neptune taken by the Voyager 2. (Courtesy of NASA)
(63K JPG)

This is an image showing the disappearance of the Great Dark Spot taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. The second picture was taken about 9 hours later showing the opposite hemisphere. (Courtesy of NASA/STScI and Dr. Heidi B. Hammel)
(38K JPG)

These are three images of Neptune taken on October 10, October 18, and November 2, 1994 from the Hubble Space Telescope. (Courtesy of NASA/STScI and Dr. Heidi B. Hammel)
(109K GIF)

This is an image of Neptune showing clouds. (Courtesy of NASA)
(30K GIF)

This is an image of the Scooter taken by the Voyager 2. The Scooter is a small irregular white cloud that spins around Neptune about every 16 hours. (Courtesy of NASA)
(92K GIF)

This is a closer view of the Great Dark Spot and the Scooter. The Scooter is small and bright and to the left of the dark spot. This image was taken on the Voyager Mission in August 1989. (Courtesy of NASA)
(60K JPG)

This is a close-up view of the Great Dark Spot taken on the Voyager in August 1989. (Courtesy of NASA)
(79K JPG)

This is an image of the Small Dark Spot which is south of the Great Dark
Spot. (Courtesy of NASA)
(298K GIF)

This is an image of cirrus-type clouds in Neptune's northern hemisphere.
The clouds extend for thousands of miles. (Courtesy of NASA)
(256K
GIF)

This is true-color image of clouds east of the Great Dark Spot taken by the Voyager 2. (Courtesy of NASA/JPL)
(64K JPG)

This is an image of Neptune's twisted rings taken by Voyager 2. (Courtesy of NASA)
(75K GIF)

This is a color image of Triton taken by Voyager 2 in August 1989. Triton is Neptune's largest satellite. (Courtesy of NASA)
(162K JPG)

This is a computer generated rendering of one of the caldera type depressions on Triton taken on August 24, 1989. (Courtesy of NASA)
(96K JPG)
This is an image of Proteus, the first of six new moons discovered by Voyager 2. (Courtesy of NASA)
(32K JPG)
Go back to Mars
, Jupiter,
Mercury, Saturn,
Pluto,
Venus,
Moon,
Earth,
Asteroids,
Comets,
Sun,
Missions,
Uranus,
Astrophysical Objects