When Nature Strikes - Earthquakes
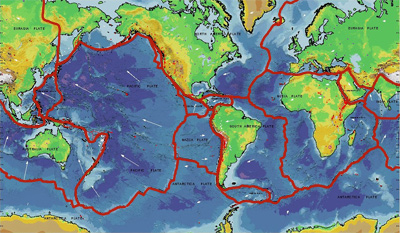
Most people know that earthquakes occur along the San Andreas Fault of California, but few realize that there is an ever greater danger lurking under the Pacific Northwest. A tectonic plate, known as the Juan de Fuca Plate, is expected to move underneath the Pacific Northwest edge of the North American continent, creating a magnitude 9 earthquake. Like the megathrust earthquake that struck Japan in 2011, the expected earthquake could topple buildings, cause the soil to behave like a liquid, and could generate a deadly tsunami. Luckily, megathrust earthquakes are infrequent. However, no one knows when the next one will strike.
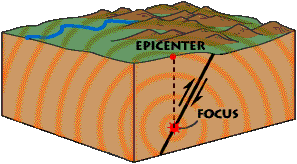
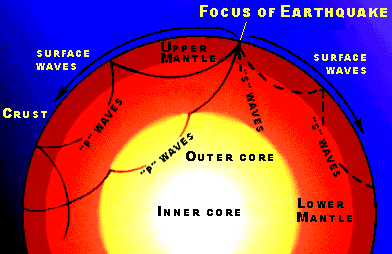
At plate boundaries, such as the boundary between the Juan de Fuca Plate and the North American Plate, plates are locked together by friction. Tectonic forces act upon the plates, adding stress that will eventually overcome the friction. As a result, the plates will finally move, releasing energy in the form of earthquake waves. By studying the tectonic forces, the history of faults and the kinds of rocks involved, scientists are searching for a way to predict when earthquakes will occur and to issue warnings.
John Vidale and his team at the Pacific Northwest Seismic Network is carefully monitoring ground motion and is helping the states of Washington and Oregon to protect citizens from the effects of a devastating magnitude 9 earthquake.
"When Nature Strikes" is produced by NBC Learn in partnership with the National Science Foundation.
When Nature Strikes: Earthquakes" Classroom Activity