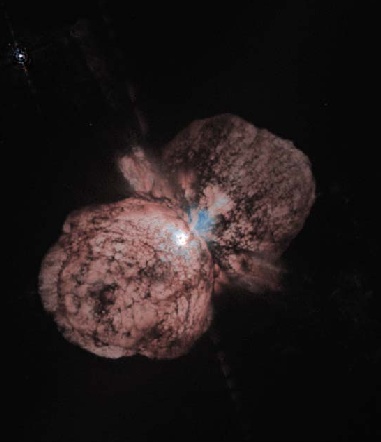
The doomed star Eta Carinae, it is blowing itself apart before it finally goes supernova
Click on image for full size
STScI
Strange Stuff In Space
There is some pretty strange stuff in space. Things that not even the strangest science fiction stories have dreamed. Some things are just so weird that even astrophysicists don't know what they are.
When stars die they go out in many different ways. When normal stars, like our sun, die they go by throwing off their outer layers and leaving behind a White Dwarf. When really massive stars die they often blow up in a huge explosion called a Supernova. Depending on how massive a star was that went supernova, a Neutron Star or a Black Hole may be left behind as a monument to the star's life.
But there are still stranger things in space. Not very long ago astronomers were baffled by the mystery of Quasars. These objects look like stars but are much farther away than stars in our galaxy and they are much brighter.
There is also a phenomenon that has caused much excitement and wonder among astronomers called Gravitational Lensing. This is where really massive things, like galaxies and galaxy clusters, actually bend light like a lens using gravity!
But one of the strangest things in space is the mystery of Gamma Ray Bursts. These are what seem to be random bursts of gamma rays, you know the radiation that made the Incredible Hulk. They come from every direction in the sky, they never repeat, and they are very energetic.
You might also be interested in:

When stars like our own sun die they will become white dwarfs. As a star like our sun is running out of fuel in its core it begins to bloat into a red giant. This will happen to our sun in 5 Billion years.
...more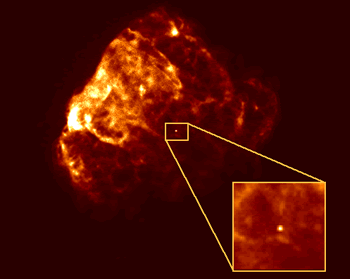
Neutron Stars are the end point of a massive star's life. When a really massive star runs out of nuclear fuel in its core the core begins to collapse under gravity. When the core collapses the entire star
...more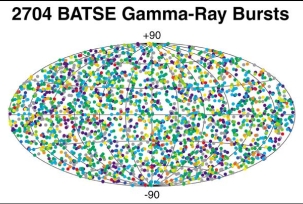
In the 1960's, the United States launched some satellites to look for very high energy light, called Gamma Rays. Gamma Rays are produced whenever a nuclear bomb explodes. The satellites found many bursts
...more
Everyone is awed by black holes. How could there be a thing that devours all light and matter around it...so that matter can never escape?!? A new discovery has been made about black holes - some of them
...more
During the early 1900's, which is not very long ago, astronomers were unaware that there were other galaxies outside our own Milky Way Galaxy. When they saw a small fuzzy patch in the sky through their
...more
Spiral galaxies may remind you of a pinwheel. They are rotating disks of mostly hydrogen gas, dust and stars. Through a telescope or binoculars, the bright nucleus of the galaxy may be visible but the
...more
What's in a Name: Arabic for "head of the demon" Claim to Fame: Represents Medusa's eye in Perseus. A special variable star that "winks" every 3 days. Type of Star: Blue-white Main Sequence Star, and
...more