Click on image for full size
Corel Photography
Salts in the Earth's early ocean
We all know that today ocean waters are very salty. Two things help scientists figure out what salt may have been part of the Earth's early oceans. Since there are very little
sedimentary rocks of ages older than 2.5 billion years (see
geologic time) that means either
- 1.) there must have been mostly igneous rocks at the beginning of time
- 2.) maybe the Earth was covered with water everywhere such that change of igneous to sedimentary rock took a long time (turbulent action in rivers and streams is required to break igneous rock apart).
Anyway, since igneous rocks are made of mostly of iron and aluminum, those were the only rocks around, and these rocks are easily destroyed by
acids in an environment with no oxygen such as that of the early Earth, the waste products of
erosion by acid, namely chlorine and iron from the rocks and the acid, had no where to go but into the ocean. Thus the early ocean was full of chrorine and iron.
What induced a change into this environment was the introduction of free oxygen due to the activity of early life. Free oxygen is an agent of change, ready to attack other molecules and react with them. In the early ocean environment, oxygen from life attacked iron from erosion.
You might also be interested in:

Eventually, photosynthesis by the earliest forms of plant life (a form of life capable of feeding itself instead of feeding off of others) began to produce significant amounts of oxygen. One important
...more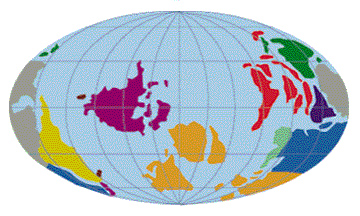
The Archean is the name of the age which began with the forming Earth. This period of Earth's history lasted a long time, 2.8 billion years! That is more than half the expected age of the Earth! And no
...more
We all know that today ocean waters are very salty. Two things help scientists figure out what salt may have been part of the Earth's early oceans. Since there are very little sedimentary rocks of ages
...more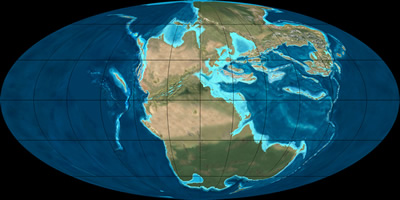
This period of time in Earth's history is a period when dinosaurs roamed the Earth. This period lasted 37 Million years. During this time, the continents we know today were combined into a giant continent
...more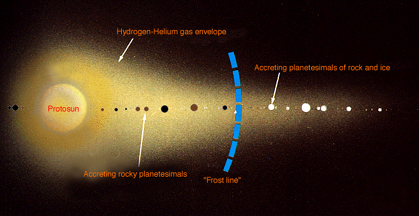
Scientists ask many questions. One of the questions they like to ask is "Where did the atmosphere come from?" As always, scientists chip in with many different, and sometimes conflicting answers. Some
...more
Once the Earth began to cool, water vapor, one of the volatiles, began to condense and form an ocean. According to the Goldilocks theory, Earth is at just the right distance from the sun for the temperature
...more
Why did the dinosaurs go extinct? No one knows for sure, and scientists have come up with a number of theories to explain why the dinosaurs suddenly died out about 65 million years ago. This extinction
...more
Altocumulus clouds are part of the Middle Cloud group (2000-7000m up). They are grayish-white with one part of the cloud darker than the other. Altocumulus clouds usually form in groups and are about
...more













