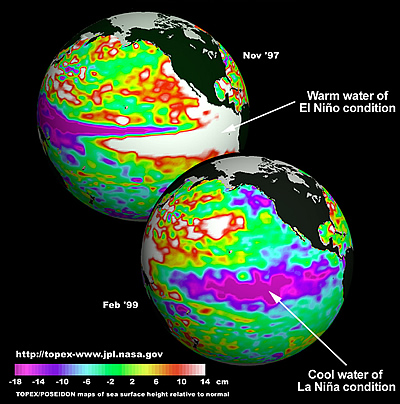
The red and white color of the eastern tropical Pacific in the upper image (from Nov. 1997) indicates higher than normal ocean level due to piling up of warm ocean water during El Nino. The lower image (Feb 1999) shows ocean level during La Nina when there is cool water from upwelling in the eastern tropical Pacific. These maps use data from TOPEX/POSEIDON and Jason 1 to show the height of the ocean surface.
Click on image for full size
Courtesy of NASA/JPL
The El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO)
Floods and mudslides in Ecuador, droughts and wildfires in Australia, and extreme California rainstorms – could all these events be related? Yes, they can. They are all affected by changes in the ocean and atmosphere called the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO).
Normally, winds move seawater at the ocean surface from the eastern part of the tropical Pacific to the western Pacific Ocean. Because the surface water is moving west, cold deep water comes to the surface in the eastern Pacific, a process called upwelling. The western Pacific is in a low pressure system and has wet weather. The eastern Pacific, in a high pressure system, is dry. But every few years the atmosphere and ocean changes during El Niño and La Niña events – the two extremes of ENSO.
During El Niño events, the difference in air pressure across the Pacific shrinks, causing the winds to weaken. Without wind pushing seawater west, the warm water of the western Pacific spreads east. Water piles up in the eastern tropical Pacific, causing the ocean surface to become higher. The extra water in the eastern Pacific causes the upwelling to weaken.
During La Niña the winds grow stronger across the Pacific because the low pressure over the western Pacific and the high pressure over the central and eastern Pacific both get larger. This causes more upwelling of ocean water in the eastern Pacific.
Both El Niño and La Niña events can have far-reaching effects. Intense rainstorms and flooding, extreme droughts, the strength of the Atlantic hurricane season, and the number of winter storms in many areas of the world are affected by ENSO events. ENSO may also have an impact on the North Atlantic Oscillation. These impacts are called teleconnections.
You might also be interested in:

Wind is moving air. Warm air rises, and cool air comes in to take its place. This movement creates different pressures in the atmosphere which creates the winds around the globe. Since the Earth spins,
...more
There are places in the ocean where water from the deep sea travels up to the surface. These are called areas of upwelling. The deep waters can have a large influence upon life in the ocean and the climate
...more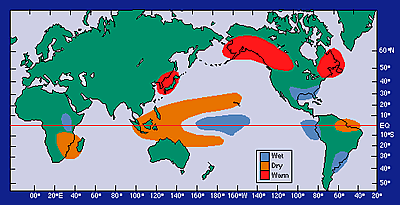
Changes in the atmosphere in one place can affect weather over 1000 miles away. Scientists are trying to sort out how this works so that they can better understand and predict weather patterns worldwide.
...more
Sometimes there is a change in the way air moves through parts of the atmosphere. And there are sometimes changes in the way water moves through the ocean too. This disturbs typical weather patterns, or
...more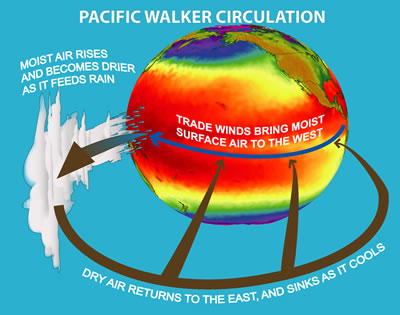
The Walker circulation is an ocean-based system of air circulation that influences weather on the Earth. The Walker circulation is the result of a difference in surface pressure and temperature over the
...more
Scientists at the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) have found a connection between solar activity and climate changes on earth. Their research may lead to the ability to predict how the
...more
If you like anchovies on your pizza, there is a good chance that the little fish now swimming in tomato sauce was once swimming in the Southeast Pacific Ocean. It was probably caught off the coasts of
...more