Click on image for full size
Courtesy Wikipedia Commons
Fisheries in the Southeast Pacific Region
If you like anchovies on your pizza, there is a good chance that the little fish now swimming in tomato sauce was once swimming in the Southeast Pacific Ocean. It was probably caught off the coasts of Peru or Chile in South America. The ocean in that area has a lot of nutrients which produce lots of fish. This area is one of the most important areas for catching fish in the world.
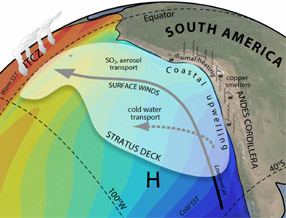
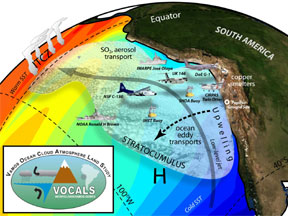
Why do fish thrive in the Southeast Pacific Ocean? It is because of the strong winds and the upwelling from the Humboldt Current. This current brings very cold water from deep in the ocean up to the surface. The waters in the deep ocean have a lot of nutrients such as nitrate and phosphate. When these nutrients come to the ocean surface they are taken up by tiny phytoplankton. Lots of nutrients mean lots of phytoplankton. The phytoplankton are at the base of the ocean food chain. If lots of phytoplankton are available as a food source, the result will be many fish and other marine life in that area.
The fishing industry has always been important to Chile and Peru. The most important species of fish are anchovies, sardines, mackerel, and salmon.
Ocean temperatures are important to all types of fish. Anchovies like cooler water so when an El Nino event happens and the ocean water is warmer, they don't do as well. Sardines like warmer water. If the temperature of the ocean goes up due to climate change, there will probably be more sardines than anchovies. One part of the VOCALS research will be to learn how changing climates might affect the fish in the Southeast Pacific Ocean.
Fish that spend all of their lives in the ocean are called pelagic fish. Anchovies and sardines are types of pelagic fish. Salmon are called anadromous fish. This type of fish starts its life in freshwater but spends most of its life in the ocean.