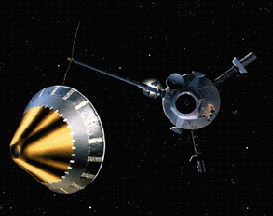
A photo of the ACE spacecraft which shows some of the instruments.
Click on image for full size
NASA
Click on image for full size
NASA
Related links:
The University of Michigan's Solar and Heliospheric Research Group The official ACE SWICS/SWIMS site
ACE Instrumentation Page
The ACE spacecraft consists of a two-deck irregular octagon, about 1.6 meters (65 inches) across and about 1 meter (40 inches) high. Eight of the scientific instruments which measure a variety of particle types are mounted to the main body of the satellite. Attached to the solar panels is the ninth instrument (see table below...), a pair of magnetometers.
| Instrument | Acronym | Principal Investigator |
|---|---|---|
| Cosmic Ray Isotope Spectrometer | CRIS | Caltech, Washington University, GSFC, JPL, University of Chicago |
| Electron, Proton and Alpha Monitor | EPAM | JHU/APL |
| Magnetometer | MAG | UD/Bartol Research Institute, GSFC |
| Solar Energetic Particle Ionic Charge Analyzer | SEPICA | University of New Hampshire, Max Planck Institute |
| Solar Wind Electon, Proton, and Alpha Monitor | SWEPAM | Los Alamos Laboratory |
| Solar Wind Ionic Charge Spectrometer | SWICS | University of Maryland, University of Bern |
| Solar Wind Ion Mass Spectrometer | SWIMS | University of Maryland, University of Bern |
| Ultra Low Energy Isotope Spectrometer | ULEIS | JHU/APL, University of Maryland |
What's New on the Site?
When Nature Strikes - Earthquakes
When Nature Strikes - Volcanoes
When Nature Strikes: Tsunami Classroom Activity
When Nature Strikes: Wildfires - Why are they a challenge to stop?
Windows to the Universe Community | |
News | Opportunities |
You might also be interested in:

Traveling Nitrogen Classroom Activity Kit
Check out our online store - minerals, fossils, books, activities, jewelry, and household items!...more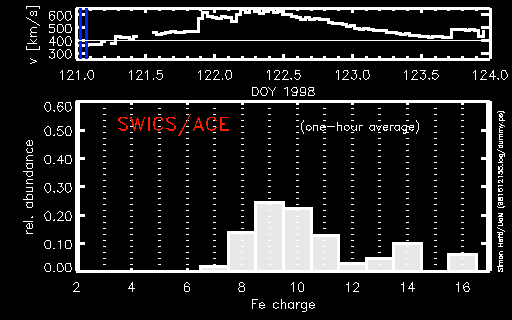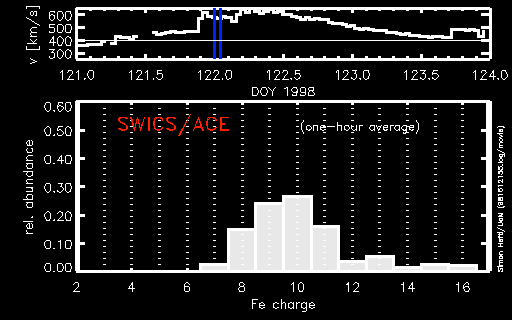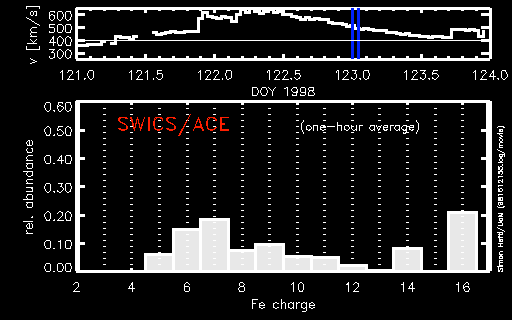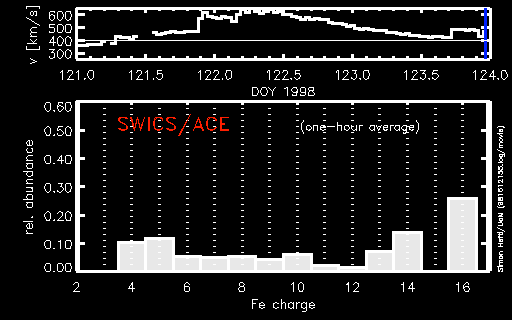
More on Recent Coronal Mass Ejection
During a period of about two days in early May, 1998, the ACE spacecraft was immersed in plasma associated with a coronal mass ejection (CME). The SWICS instrument on ACE, which determines unambiguously...more
Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) was one of the most important exploration tools of the past two decades, and will continue to serve as a great resource well into the new millennium. The HST is credited...more
Apollo 11
Driven by a recent surge in space research, the Apollo program hoped to add to the accomplishments of the Lunar Orbiter and Surveyor missions of the late 1960's. Apollo 11 was the first mission to succeed...more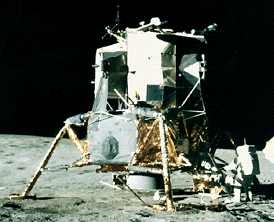
Apollo 12
Apollo 12 survived a lightning strike during its launch on Nov. 14, 1969, and arrived at the Moon three days later. Astronauts Charles Conrad and Alan Bean descended to the surface, while Richard Gordon...more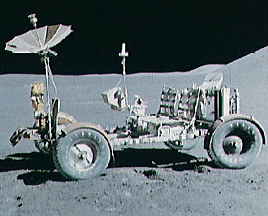
Apollo 15
Apollo 15 marked the start of a new series of missions from the Apollo space program, each capable of exploring more lunar terrain than ever before. Launched on July 26, 1971, Apollo 15 reached the Moon...more
Deep Impact Mission
NASA chose Deep Impact to be part of a special series called the Discovery Program on July 7, 1999. In May 2001, Deep Impact was given the "go" from NASA to start with mission development. Deep Impact...morePlease log in
Science Blogs
Real Climate: climate science from climate scientists

Windows to the Universe, a project of the National Earth Science Teachers Association, is sponsored in part is sponsored in part through grants from federal agencies (NASA and NOAA), and partnerships with affiliated organizations, including the American Geophysical Union, the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, the Earth System Information Partnership, the American Meteorological Society, the National Center for Science Education, and TERC. The American Geophysical Union and the American Geosciences Institute are Windows to the Universe Founding Partners. NESTA welcomes new Institutional Affiliates in support of our ongoing programs, as well as collaborations on new projects. Contact NESTA for more information.