Click on image for full size
Image courtesy of NASA
Earth as a System
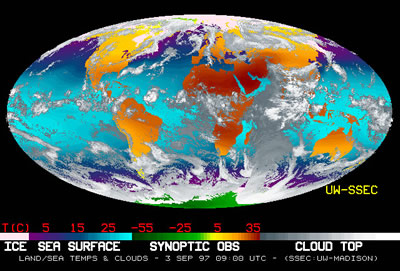
The first time people got a glimpse of the whole Earth was December 1968. Apollo 8 astronauts, en route to and from the Moon, took pictures of the Earth from space. In their photographs, the Earth looks like a small blue and white orb in a sea of black space. Looking at the planet from that vantage point it's easy to see that all its components- the living things, the air, the water, the ice, and the rocks - are connected. Everything on Earth is in the same boat floating through space - a system.
Since the 1980s, NASA scientists have been studying the Earth as they study other planets - mainly from above with satellites. Based on this way of looking at Earth, they developed the idea of Earth system science.
"From space we can view the Earth as a whole system, observe the net results of complex interactions, and begin to understand how the planet is changing in response to natural and human influences," NASA explained in its 2003 Earth Science Enterprise report.
There are five parts of the Earth system, often known as "spheres." Each part has its own collection of materials and dynamic processes that make Earth an ever-changing place. However, each part of the Earth system does not operate on its own. They all interact with other parts in many ways.
- The atmosphere extends up from the Earth surface for several hundred kilometers. The lowest part is home to clouds and weather.
- The biosphere is all living things including plants, animals, protists, fungi, Achaea, and bacteria.
- The geosphere generally extends from the Earth surface to its core including all rocks, molten rock, sediments, and soils (although there are important living components to soils as well).
- The hydrosphere includes the ocean, rivers, lakes, streams, groundwater, water vapor, and even puddles.
- The cryosphere is the frozen part of the Earth system and includes icy aspects of our planet like snow, glaciers, and sea ice.
The Sun, although not literally part of the Earth, has a large impact on the Earth and so it is also considered a part of the Earth system too. Almost all the energy on Earth is derived from the Sun. The factors outside the planet, like the Sun and solar system, which have an impact on the Earth system, are sometimes collectively called the Exosphere.