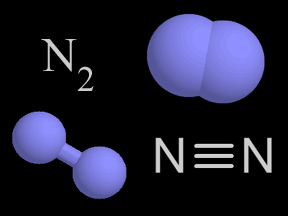This image of Titan's atmosphere was captured by NASA's Cassini spacecraft on July 3, 2004. The orange color of Titan is shown roughly as our eyes would see it. A layer of haze, composed of complex organic molecules, is shown in purple in this image. The false-color representation of the haze layer, which hovers a few hundred km above the moon's surface, indicates that it was imaged in ultraviolet "light".
Click on image for full size
Image courtesy NASA/JPL/Space Science Institute.
The Atmosphere of Titan
Titan is the only moon in our Solar System with a significant atmosphere.
Titan's atmosphere consists mostly of nitrogen, and is so thick that the atmospheric
pressure at the moon's surface is about 60% greater than Earth's atmospheric
pressure.
Titan's atmosphere also has a significant amount of methane. Bombardment of
the methane by solar ultraviolet radiation has produced trace amounts of numerous
other hydrocarbons. These organic molecules create several layers of smog-like
haze in the moon's atmosphere, obscuring views of Titan's
surface.
The Cassini spacecraft has observed clouds in Titan's atmosphere near the moon's
poles. Temperatures are so cold (-178º C, -288º F) on Titan that methane
is a liquid at the surface. Scientists believe that methane and ethane may
fall as rain and snow from the clouds in Titan's atmosphere onto its frigid surface. This
image shows the predicted structure of Titan's atmosphere. New results from the Huygens
probe will likely revise our knowledge of the structure and composition of Titan's atmosphere.
You might also be interested in:
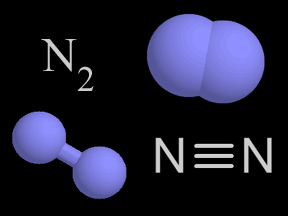
Nitrogen is a chemical element with an atomic number of 7 (it has seven protons in its nucleus). Molecular nitrogen (N2) is a very common chemical compound in which two nitrogen atoms are tightly bound
...more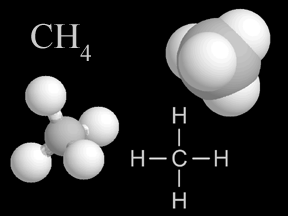
Methane is gas that is found in small quantities in Earth's atmosphere. Methane is the simplest hydrocarbon, consisting of one carbon atom and four hydrogen atoms. Methane is a powerful greenhouse gas.
...more
There is a large class of important chemical compounds whose molecules are made up entirely of carbon and hydrogen atoms. These compounds, as a group, are called "hydrocarbons". Hydrocarbons are the critical
...more
Smog is a type of air pollution. Smog is a mixture of smoke and fog, hence the name (SMoke + fOG = SMOG). Victorian-era London was famous for its thick smogs, which resulted from the city's frequent, naturally
...more
The Cassini probe began its journey to Saturn on October 15, 1997. It flew by Earth in August, 1999, before heading towards the distant planet. Cassini passed Jupiter in 2000 and then burned towards its
...more
Titan is Saturn's largest moon, and the second largest moon in our Solar System. It is the only moon with a thick atmosphere. Titan's poles are interesting places. Scientists have discovered lakes at both
...more
Titan's atmosphere is a lot like the Earth's, except that it is very cold, from -330 degrees to -290 degrees! Like the Earth, there is a lot of Nitrogen and other complex molecules. There also may be an
...more