Click on image for full size
Image courtesy W. M. Keck Observatory.
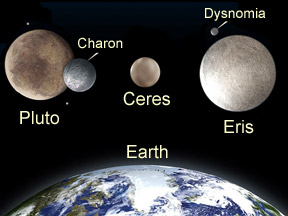
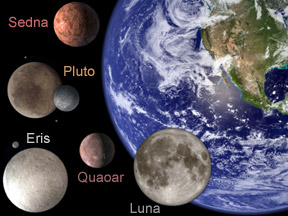
Eris - a dwarf planet
Eris is a dwarf planet that was discovered in 2005. Eris is a trans-Neptunian object (TNO) that orbits the Sun on the frozen fringes of our Solar System beyond the Kuiper Belt. Eris takes 557 years to travel once around the Sun along its highly elliptical orbit. We don't yet have any clear images of the surface of Eris because it is so far away. Astronomers aren't yet certain how long a day on Eris is; they think it lasts at least eight hours.
Eris is slightly larger than Pluto, having a diameter somewhere between 2,400 and 3,000 km (1,491 and 1,864 miles). The discovery of Eris brought to a head a debate among astronomers as to whether Pluto should be considered a true planet. In 2006 the International Astronomical Union (IAU) declared that Pluto, Eris, and Ceres are the first three members of a new class called "dwarf planets".
Eris was photographed in October 2003, but, because of its slow rate of motion, wasn't recognized as a KBO until January 2005. The object's discovery was officially announced on July 29, 2005, by the scientists who found it (Michael Brown, Chad Trujillo, and David Rabinowitz).
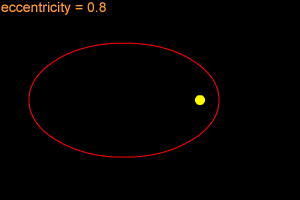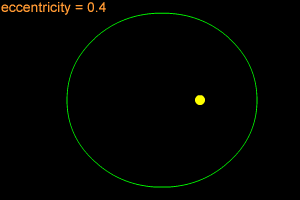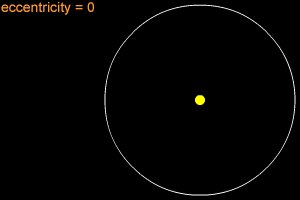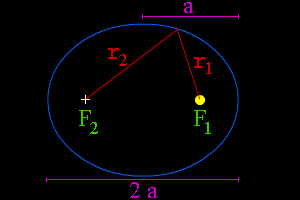
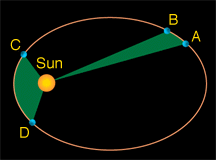
Eris has an unusual orbit. The orbit is tilted at an angle of 44° with respect to the ecliptic, the imaginary plane in which Earth and most other planets move. The orbit is highly eccentric (e = 0.44), bringing the object within 38 AU of the Sun at perihelion and sending it out beyond 97 AU at aphelion. Eris takes 557 years to orbit the Sun at an average distance (semi-major axis) of 68 AU.
Eris has a moderate-sized moon which was first spotted in September 2005. The moon has been given the name Dysnomia.
When Eris was first discovered, it bore the temporary designation of 2003 UB313. Astronomers nicknamed it "Xena", after the title character of the television show "Xena: Warrior Princess". The moon was nicknamed "Gabrielle" after Xena's sidekick in the TV series. The name Eris now supercedes all prior designations.