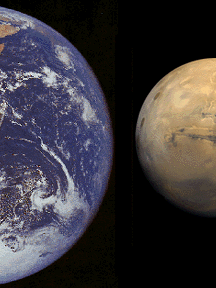
This image shows the Earth and Mars
NASA
An Overview of the History of Mars
The terrestrial planets formed by accretion of rocky material and volatiles out of the primitive solar nebula. As they finished forming, about 4 Billion Years ago, the surface continued to be bombarded by the remanent of planetary material available nearby. This period is called the Period of Late, Heavy Bombardment. During this time, there was probably abundant water on the surface of Mars, and under ground. There was probably volcanic activity as well as plate tectonics. From the Period of Late, Heavy Bombardment forward, this is probably what happened to Mars:
The changes in climate probably persist to the present day, but the rest of the history of Mars was finished 3.5 Billion Years ago.
The reasons these things happened to Mars, and not to the Earth or Venus has to do with the small size of Mars, and the fact that Mars is farther from the sun that either the Earth or Venus. Some scientists call this the "Goldilocks" phenomenon.
You might also be interested in:

How did life evolve on Earth? The answer to this question can help us understand our past and prepare for our future. Although evolution provides credible and reliable answers, polls show that many people turn away from science, seeking other explanations with which they are more comfortable.
...more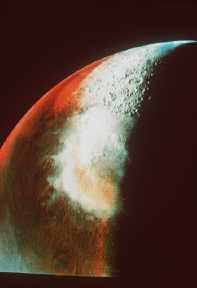
The terrestrial planets formed about 4 Billion Years ago. As the process which formed them came to an end, the planets may have been left in either of the following two states: very warm, with a softer
...more
Many of the reasons the history of Mars is different from that of the Earth stem from the small size of Mars. Mars is about 1/3 the size of the Earth. This means that it was able to cool much more rapidly
...more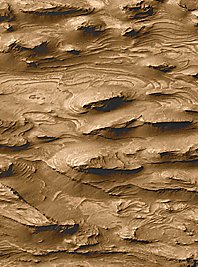
The Mars Global Surveyor (MGS) was launched on November 7, 1996. It has been in orbit around Mars for over 1500 days. It may have made its greatest observation this month! High-resolution pictures taken
...more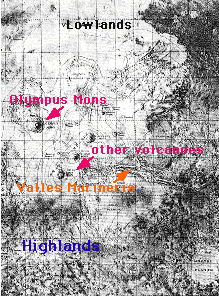
The surface of Mars can be broken into two main regions: highlands and lowlands. The highlands are in the southern hemisphere (the bottom of the figure), and the lowlands are in the northern hemisphere
...more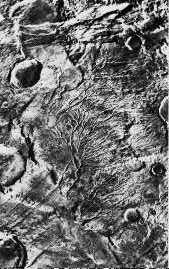
The presence of water near the surface of Mars, or lack of water, is a big factor in determining the climate of Mars, and the suitability of Mars to support life. Finding out what has happened to the water
...more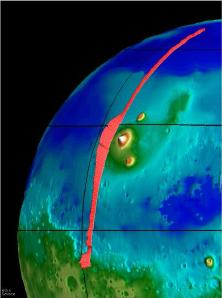
This image, taken from the Mars Global Surveyor mission (MGS), shows the Tharsis Ridge, the green/blue area in the middle of the picture, as well as a portion of the southern hemisphere of Mars. The green
...more
High resolution images returned by the Mars Global Surveyor spacecraft allow closer examination of this unusual canyon. As shown here, slopes seem to descend steeply to the north and south in broad, debris-filled
...more