Click on image for full size
Image courtesy of NOAA. Public domain.
What Is Climate?
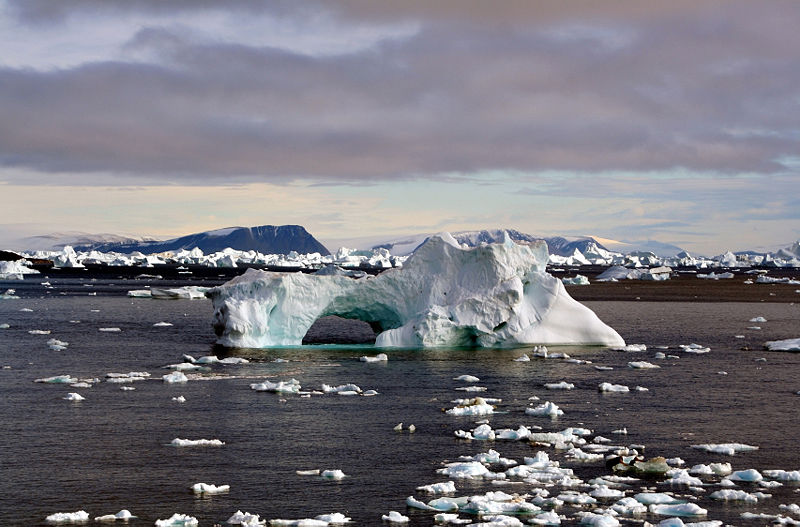
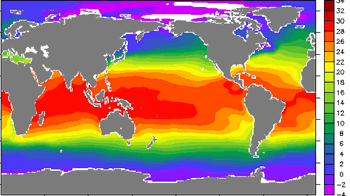
The climate where you live is called regional climate. It is the average weather in a place over more than thirty years. To describe the regional climate of a place, people often tell what the temperatures are like over the seasons, how windy it is, and how much rain or snow falls. The climate of a region depends on many factors including the amount of sunlight it receives, its height above sea level, the shape of the land, and how close it is to oceans. Since the equator receives more sunlight than the poles, climate varies depending on distance from the equator.
However, we can also think about the climate of an entire planet. Global climate is a description of the climate of a planet as a whole, with all the regional differences averaged. Overall, global climate depends on the amount of energy received by the Sun and the amount of energy that is trapped in the system. These amounts are different for different planets. Scientists who study Earth's climate and climate change study the factors that affect the climate of our whole planet.
While the weather can change in just a few hours, climate changes over longer timeframes. Climate events, like El Nino, happen over several years, small-scale fluctuations happen over decades, and larger climate changes happen over hundreds and thousands of years. Today, climates are changing. Our Earth is warming more quickly than it has in the past according to the research of scientists. Hot summer days may be quite typical of climates in many regions of the world, but global warming is causing Earth's average global temperature to increase. The amount of solar radiation, the chemistry of the atmosphere, clouds, and the biosphere all affect Earth's climate.