This image is a montage of high resolutions photographs of the Earth taken in January 2012 by the Visible/Infrared Imager Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) instrument on the Suomi NPP satellite. The image shows many stunning details of
our home planet -
particularly at high resolution. The beauty of our planet is obvious from space - our blue
waters, our white
clouds, and the green from
life abundant at the surface.
Image courtesy of NASA
Earth's Global Climate
Earth's climate is determined by the amount of energy received from the Sun and the amount of energy held in the Earth system - in short, Earth's radiation budget.
The Sun emits an enormous amount of energy, in the form of electromagnetic radiation, into space. If we could capture all of that energy and convert it to electricity, we would have more than enough energy to fuel all our needs on this planet, by many time! Most of the Sun's energy flows out of the solar system into interstellar space without ever colliding with anything. A very small fraction of that energy collides with planets, including Earth, before it can escape into interstellar space. This tiny amount of energy from the Sun that Earth intercepts is sufficient to warm our planet and drive its climate, weather, and support life on Earth.
There are two main ways that the Sun's energy can vary at Earth - either by changes in the Earth's distance from the Sun or by changes in the amount of energy emitted from the Sun itself.
Another key factor in determining Earth's climate is the composition of the atmosphere. As the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere has increased, particularly in recent decades, our atmosphere is warming.
Finally, the amount of energy reflected away from Earth is a critical factor in determining our climate. This is called the Earth's albedo. Surfaces that reflect light - like fresh snow or clouds - reduce the amount of energy that gets into the Earth system. Because warming leads to melting of ice and snow, a feedback loop develops leading to even further reduction in ice and snow... and more warming.
You might also be interested in:

The first time people got a glimpse of the whole Earth was December 1968. Apollo 8 astronauts took pictures of the Earth as they traveled to and from the Moon. In their photographs, the Earth looks like
...more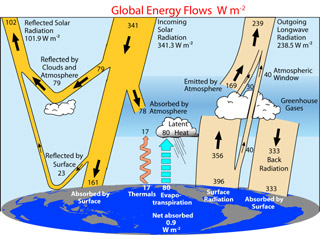
Light from the Sun shines on Earth. Some of that light reflects off clouds back into space. Some of the light makes it to the ground and warms our planet. The warm ground and oceans give off infrared (IR)
...more
Electromagnetic radiation is the result of oscillating electric and magnetic fields. The wave of energy generated by such vibrations moves through space at the speed of light. And well it should... for
...more
Even though only a tiny amount of the gases in Earth’s atmosphere are greenhouse gases, they have a huge effect on climate. There are several different types of greenhouse gases. The major ones are carbon
...more
This picture of the Earth surface was taken from high above the planet in the International Space Station. In this view from above, we can see that there are lots of different things that cover the Earth.
...more
The climate at a given location on Earth is the regional climate. Regional climate depends on the temperature, precipitation, and winds experienced over the long term at that location. These characteristics
...more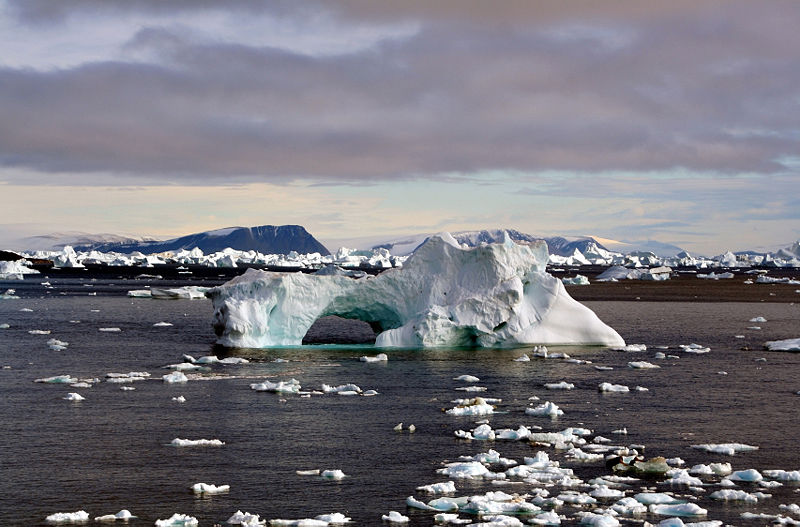
Climate change refers to changes in global or regional climate determined over a long term - typically a minimum of 30 years. A short-term weather event such as an intense storm or heat wave are a normal
...more















