Exploratour - Evolution of the Solar System
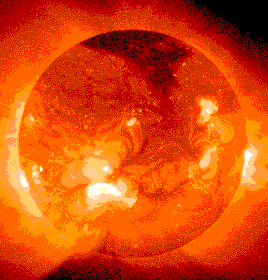
A star that is newly born like this is in a childhood phase called the T-Tauri phase. During its T-Tauri phase, when the Sun first started shining, it was not very bright. But it was very powerful, nevertheless, and spit out a stream of particles into space. The sun still spits out this stream of particles, today, in a much less powerful form. It is called the "solar wind". The magnetospheres of most of the planets protects the planets from the effects of these very energetic (and therefore dangerous) particles.
But the force of T-Tauri "wind" was probably enough to take away of whatever atmosphere had been gathered from the solar nebula around Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. On the other hand, because of their larger size and greater ability to hold an atmosphere with the force of gravity, this wind did not have enough force to remove the atmospheres from Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.
This is page 24 of 60