This image of the asteroid Ceres was made by the Hubble Space Telescope in December 2003 and January 2004. Ceres was declared a "dwarf planet", along with Pluto and Eris, in 2006.
Click on image for full size
Image courtesy of NASA, ESA, J. Parker (Southwest Research Institute), P. Thomas (Cornell University), L. McFadden (University of Maryland, College Park), and M. Mutchler and Z. Levay (STScI).
Ceres: Asteroid and Dwarf Planet
Ceres is the largest asteroid in the main asteroid belt. It was classified as a "dwarf planet" in 2006, along with Pluto and Eris. Ceres was discovered on January 1, 1801 by the Italian astronomer and monk Giuseppe Piazzi.
Ceres has a diameter of about 975 km (605 miles). It is by far the largest and most massive body in the main asteroid belt, and contains about a third of the belt's total mass. Ceres orbits the Sun once every 4.6 years. Its orbit lies between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. The asteroid turns on its axis once every 9 hours, so that's how long a day is on Ceres.
You might also be interested in:
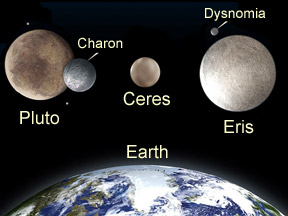
In 2006 the International Astronomical Union (IAU) approved a new classification scheme for planets and smaller objects in our Solar System. Their scheme includes three classes of objects: "small solar
...more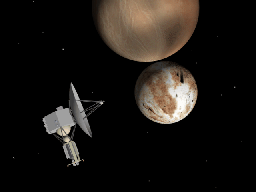
Pluto is a frigid ball of ice and rock that orbits far from the Sun on the frozen fringes of our Solar System. Considered a planet, though a rather odd one, from its discovery in 1930 until 2006, it was
...more
Eris is a dwarf planet that was discovered in 2005. Eris is a trans-Neptunian object (TNO) that orbits the Sun on the frozen fringes of our Solar System beyond the Kuiper Belt. Eris takes 557 years to
...more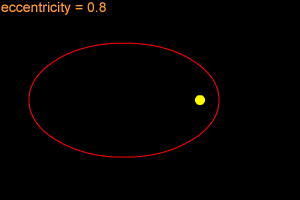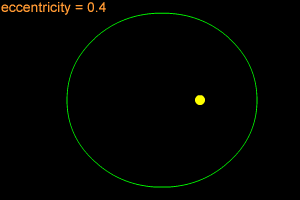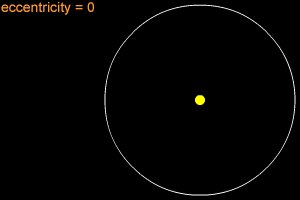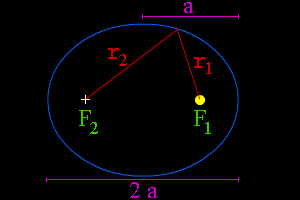
When one object is in orbit around another object, the orbit is usually an elliptical orbit. For example, all of the planets in our Solar System move around the Sun in elliptical orbits. An ellipse is
...more
Makemake is a dwarf planet in our Solar System. Makemake was discovered on March 31, 2005 by a team of astronomers led by Mike Brown of the California Institute of Technology. The International Astronomical
...more
Toutatis is a very odd asteroid. It appears to be two asteroids that are either loosely stuck together, rolling around against each other, or orbiting very close to one another. The orbit of Toutatis crosses
...more
Lutetia is a medium-sized asteroid which orbits in the main asteroid belt between the planets Mars and Jupiter. It is officially known as "21 Lutetia" because it was the 21st asteroid discovered. The asteroid
...more















