The Coma Cluster of Galaxies
Click on image for full size
Courtesy of NASA.
Elliptical Galaxies
Elliptical galaxies are generally egg-shaped. If you have the chance
to see one through a small telescope, it will probably look just like
a fuzzy smudge to you, a piece of lint. But it is really formed of
many billions of stars orbitting the center of the galaxy.
Each elliptical galaxy is assigned a number ranging from 0 to 7 which
represents how elliptical it is. The most elliptical galaxies are a
7, while a galaxy which appears circular is a 0. Their shape may tell
us something about how the galaxies formed and evolved. Elliptical
galaxies also come in a range of sizes from giants, which are very
massive and bright, to dwarfs, which are small but which may be very
numerous. In fact, ellipticals are both the largest and smallest
galaxies known!
We think of ellipticals as old because they have not formed any new
stars recently, unlike spiral
galaxies which are forming new stars even now. They appear not to
have very much cool gas or dust from which to form stars.
Elliptical galaxies are the dominant type of galaxy in most clusters
and groups of galaxies. In our own Local Group, for example, there
are no large ellipticals, but many dwarf ellipticals orbiting both the
Milky Way and the Andromeda galaxy.
You might also be interested in:

Spiral galaxies may remind you of pinwheels turning slowly as though in some intergalactic breeze. They are rotating disks of gas, dust and stars. Through a telescope or binoculars, the bright nucleus
...more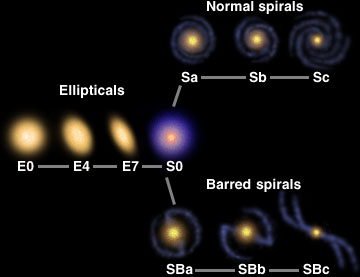
The introduction of telescopes to the study of astronomy opened up the universe, but it took some time for astronomers to realize how vast the universe could be. Telescopes revealed that our night sky
...more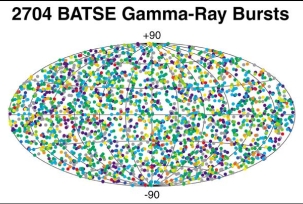
In the 1960's, the United States launched a series of satellites to look for very high energy photons, called Gamma Rays, that are produced whenever a nuclear bomb explodes. These satellites soon detected
...more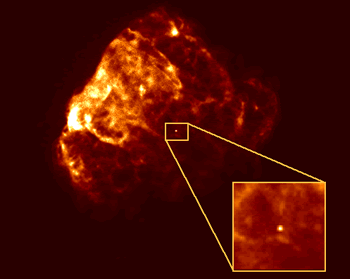
Neutron Stars are the end point of a massive star's life. When a really massive star runs out of nuclear fuel in its core the core begins to collapse under gravity. When the core collapses the entire star
...more
White Dwarfs are the remnants of stars that were massive enough to stay alive using nuclear fusion in their cores, but not massive enough to blow apart in a Type II supernova. When stars like our own sun
...more
What's in a Name: Arabic for "head of the demon" Claim to Fame: Represents Medusa's eye in Perseus. A special variable star that "winks" every 3 days. Type of Star: Blue-white Main Sequence Star, and
...more
What's in a Name: Nicknamed the "Pup" because it is the companion to Sirius, "the Dog Star" Claim to Fame: Highly compressed white dwarf remnant. Density about 50,000 times that of water. It has approximately
...more















