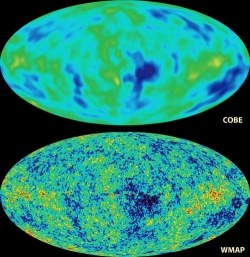
A detailed view of the Cosmic Microwave Background from WMAP, compared to the original view from the COBE satellite.
Click on image for full size
NASA/WMAP Science Team
The Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation
In the 1960's another startling discovery was made quite by
accident. A pair of scientists at Bell Laboratories detected some
annoying background noise using a special low noise antenna. The
strange thing about the noise was that it was coming from every
direction and did not seem to vary in intensity at all. They had
discovered the Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation.
This radiation permeates the entire Universe and is no stronger or
weaker in any direction. It has a perfect blackbody spectrum,
meaning it behaves like radiation from an object that absorbs and
emits all radiation that falls upon it. Its temperature is 2.7 degrees
Kelvin (-454.81 degrees Farenheit). It has only minute fluctuations
that were only detectable by the very sensitive space craft the Cosmic
Background Explorer, COBE. This radiation is believed to be the
remanant of the Universe's brilliant beginning, known as the Big Bang.
More recently, the Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) team has made a
more detailed full-sky map of this oldest light in the universe. The WMAP image
brings the COBE picture into sharp focus, and provides firm answers to age-old
questions. WMAP resolves slight temperature fluctuations, which vary by only
a few millionths of a degree. These new data support and strengthen the Big Bang
and Inflation Theories.
You might also be interested in:

According to the Big Bang theory, the universe began about 12-14 billion years ago. Right after the Big Bang, the universe was really hot! But, as the universe has expanded, the particles within the universe
...more
Some of the best news of the week is that the Microwave Anisotropy Probe (MAP) was launched successfully last Saturday! Liftoff on its Delta II rocket occurred on time at 15:46:46 EDT, June 30, 2001. So
...more
NASA scientists have taken a "snapshot" picture of the oldest light in the universe. The image shows the remains of light emitted during the big bang, which is now microwave energy. The light
...more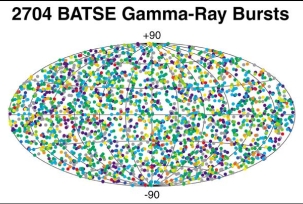
In the 1960's, the United States launched a series of satellites to look for very high energy photons, called Gamma Rays, that are produced whenever a nuclear bomb explodes. These satellites soon detected
...more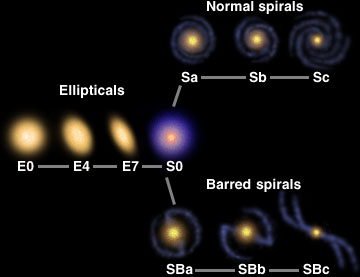
The introduction of telescopes to the study of astronomy opened up the universe, but it took some time for astronomers to realize how vast the universe could be. Telescopes revealed that our night sky
...more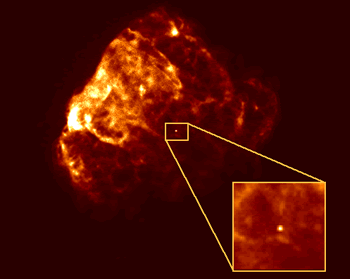
Neutron Stars are the end point of a massive star's life. When a really massive star runs out of nuclear fuel in its core the core begins to collapse under gravity. When the core collapses the entire star
...more
Spiral galaxies may remind you of pinwheels turning slowly as though in some intergalactic breeze. They are rotating disks of gas, dust and stars. Through a telescope or binoculars, the bright nucleus
...more