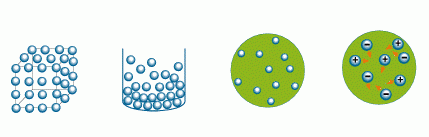
This image illustrates the four common states of matter: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma.
General Atomics
States of Matter
This figure shows the four common states of matter: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma.
Consider water as an example. Solid water is ice. Liquid water is, well, water. We call water in its gaseous form "water vapor". A plasma created from water would include electrons, protons (hydrogen atom nuclei), and oxygen atom nuclei (protons and neutrons).
There are special names for most transitions from one state to another. Freezing is turning from a liquid to a solid; melting is turning from a solid to a liquid. The transition from liquid to gas can happen by boiling or evaporation. Condensation is changing from a gas to a liquid. Sometimes (usually at low pressure) a solid can become a gas directly (without first melting to become a liquid); this transformation is called "sublimation". Removing electrons from atoms (usually in a gas) to produce a plasma is called "ionization".
Stars are made of plasma, so plasma is the most abundant form of matter in the
universe.
There are several other very exotic and unusual forms of matter that we don't encounter in daily life. A Bose-Einstein condensate can only form at temperature near absolute zero, and was first created in a lab in 1995. Degenerate matter can come into being under incredibly high pressure inside white dwarf and neutron stars. There are other very strange, very rare forms of matter as well.
You might also be interested in:

Solid is one of the four common states of matter. The three others are gas, liquid, and plasma. There are also some other exotic states of matter that have been discovered in recent years. Unlike liquids
...more
Plasma is known as the fourth state of matter (the first three states being solid, liquid and gas).Matter in ordinary conditions on Earth has electrons that orbit around the atomic nucleus. The electrons
...more
The cryosphere includes the parts of the Earth system where water is in its frozen (solid) form. This includes snow, sea ice, icebergs, ice shelves, glaciers, ice sheets, and permafrost soils. Approximately
...more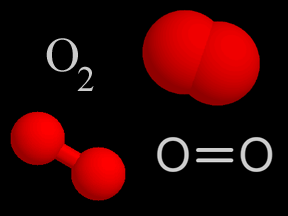
Oxygen is a chemical element with an atomic number of 8 (it has eight protons in its nucleus). Oxygen forms a chemical compound (O2) of two atoms which is a colorless gas at normal temperatures and pressures.
...more
Any substance, called matter, can exist as a solid material, liquid, or gas. These three different forms are called states. Matter can change its state when heated. As a solid, matter has a fixed volume
...more
One process which transfers water from the ground back to the atmosphere is evaporation. Evaporation is when water passes from a liquid phase to a gas phase. Rates of evaporation of water depend on factors
...more
White Dwarfs are the remnants of stars that were massive enough to stay alive using nuclear fusion in their cores, but not massive enough to blow apart in a Type II supernova. When stars like our own sun
...more