Sponges, corals, and gorgonians living in a reef at the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary
Click on image for full size
Courtesy of NOAA
Life in the Shallow Ocean
Many creatures make their home at the bottom of the ocean where the water is shallow enough for sunlight to reach them.
Where the ocean floor is sandy or muddy, you might find fast-moving crabs and slow-moving sea stars and snails. Some fish and sharks swim about just above the ocean floor. Other animals, like clams, worms, and sea urchins, live buried in the sand or mud. Sea grass, which looks like a lawn of tall grass, can also grow in here.
Where the ocean floor is rocky and water is cold, kelp forests can grow. In these places you will find large algae called kelp growing from the ocean floor all the way to the surface of the water. The kelp makes an underwater forest where many different animals live. You might find sea lions swimming between kelp in search of fish or playful sea otters eating urchins and molluscs called abalone.
In tropical, warm water coral reefs grow on rocky areas of the ocean floor. Coral reefs are named after coral animals. Reefs are full of hundreds of other types of animals and algae too. You can find lots of colorful fish swimming through reefs. On the surface of the reef you can find invertebrates like sponges, snails, sea fans, worms, crabs, and sea stars.
Last modified June 1, 2010 by Lisa Gardiner.
You might also be interested in:

Scientists have been studying the head of a very interesting fossil animal. The animal was large and had a flattened head and body. It lived in shallow water 375-million-years-ago. It was a bit like the
...more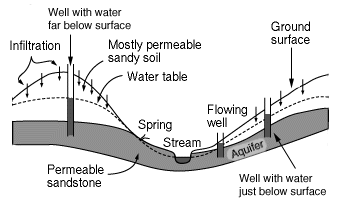
An aquifer is the name for a layer of rock which is capable of holding a large amount of water. Some layers are better at holding water than others, for example a layer of sandstone can hold a good deal
...more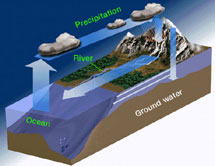
Limestone is an example of a carbonate. Other examples of carbonates include calcite, dolomite, and marble. Limestone dissolves easily in rainwater, especially rainwater which is loaded with carbonic acid.
...more
Have you ever left a glass of water out for a long time? Did you notice that the water disappears after a few days? That's because it evaporated! Evaporation is when water passes from a liquid to a gas.
...more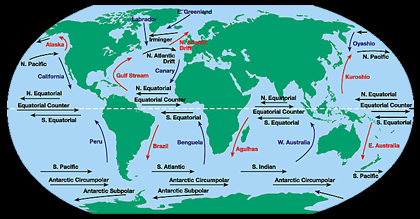
The water at the ocean surface is moved by powerful wind. The wind is able to move the top 400 meters of the ocean. This moving water is called surface ocean currents. Surface ocean currents form large
...more
Rivers are very important to Earth because they are major forces that shape the landscape. Also, they provide transportation and water for drinking, washing and farming. Rivers can flow on land or underground
...more
Almost 3/4 of the Earth is covered with water. Almost all of that water is in the oceans. Have you ever been swimming in the ocean? If you have and you accidentally got water in your mouth, you know the
...more















