This fossil fish bridges the evolutionary gap between animals of land and sea.
Click on image for full size
Courtesy of Zina Deretsky, National Science Foundation
Details of Evolutionary Transition from Fish to Land Animals Revealed
News story originally written on October 15, 2008
Scientists have been studying the head of a very interesting fossil animal.
The animal was large and had a flattened head and body. It lived in shallow water 375-million-years-ago.
It was a bit like the first four-footed animals that lived on land. And it was also a bit like fish that live in the water. It had scales and fins. The scientists think that the animal lived on the bottom in shallow water. It may have been able to get out of the water sometimes too.
It took more than a year for scientists to get the fossil head skeleton out of the surrounding sedimentary rock. Once they did, they found that the head had a flat skull and a long snout, much like some land animals. The scientists suspect that these features helped the animal survive in shallow water.
Last modified January 16, 2009 by Lisa Gardiner.
You might also be interested in:

Fossils are evidence of what life was like long ago. The oldest fossils are over three billion years old and the youngest fossils are about 10,000 years old. Scientists that study fossils know that creatures
...more
Scientists have learned that Mount Hood, Oregon's tallest mountain, has erupted in the past due to the mixing of two different types of magma. Adam Kent, a geologist at Oregon State University, says this
...more
The Earth's mantle is a rocky, solid shell that is between the Earth's crust and the outer core. The mantle is made up of many different reservoirs that have different chemical compositions. Scientists
...more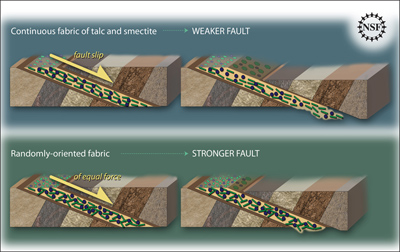
Some faults look strong and like they wouldn’t cause an earthquake. But it turns out that they can slip and slide like weak faults causing earthquakes. Scientists have been looking at one of these faults
...more
The sun goes through cycles that last approximately 11 years. These solar cycle include phases with more magnetic activity, sunspots, and solar flares. They also include phases with less activity. The
...more
Studying tree rings doesn't only tell us the age of that tree. Tree rings also show what climate was like while the tree was alive. This means that tree rings can tell us about climates of the past. Two
...more
Earth's first life form may have developed between the layers of a chunk of mica sitting like a multilayered sandwich in primordial waters, according to a new hypothesis. The mica hypothesis, which was
...more















