The carbon cycle, one of Earth's biogeochemical cycles.
Click on image for full size
NCAR
Biogeochemical Cycles
As a part of biogeochemical cycles, certain elements move through both living and non-living components of the Earth system. The living parts of the Earth system comprise the biosphere, while the non-living parts of the Earth include the hydrosphere, atmosphere, cryosphere, and geosphere. The same individual elements are recycled over and over in different parts of the Earth through biogeochemical cycles.
For example, carbon may be taken from the air (atmosphere) into the ocean surface (hydrosphere) where it is utilized by photosynthesizing plankton (biosphere). Carbon is also stored long-term in rocks (geosphere) and fossil fuels like oil, coal, and natural gas (biosphere). This long-term storage that sequesters an element from the rest of the cycle for some amount of time is called a “sink”. When fossil fuels are burned, carbon that had been sequestered underground is sent into the air (atmosphere) as carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas.
All chemical elements that are found in living things are a part of biogeochemical cycles, the most common of these being carbon and nitrogen.
Find out more about two common biogeochemical cycles!
In recent decades these biogeochemical cycles have been changing because of how humans are changing the biosphere (see links below). Less forests, more factories and cars that burn fossil fuels - these changes to biogeochemical cycles are causing more greenhouse gases in our atmosphere and, thus, more global warming.
Last modified May 7, 2007 by Lisa Gardiner.
You might also be interested in:

The cryosphere includes the parts of the Earth system where water is in its frozen (solid) form. This includes snow, sea ice, icebergs, ice shelves, glaciers, ice sheets, and permafrost soils. Approximately
...more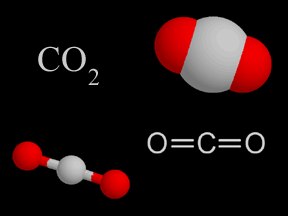
Carbon dioxide is a colorless and non-flammable gas at normal temperature and pressure. Although much less abundant than nitrogen and oxygen in Earth's atmosphere, carbon dioxide is an important constituent
...more
Less than 1% of the gases in Earth's atmosphere are called greenhouse gases. Even though they are not very abundant, these greenhouse gases have a major effect. Carbon dioxide (CO2), water vapor (H2O),
...more
The world's surface air temperature increased an average of 0.6° Celsius (1.1°F) during the last century according to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). This may not sound like very
...more
Look up into the sky and you look through millions of air molecules, eighty percent of which are nitrogen molecules, two atoms of nitrogen bonded together. Nitrogen is found all over the planet, not just
...more
Plants need nitrogen. It is a nutrient that allows them to grow larger and faster. Plants are not able to make use of the nitrogen gas in the atmosphere, two nitrogen atoms bonded together. It is not a
...more
Chemistry is the study of matter, energy, and their interactions. Chemists study the composition of substances, their properties, and how they react with each other under varying circumstances. Indeed,
...more















