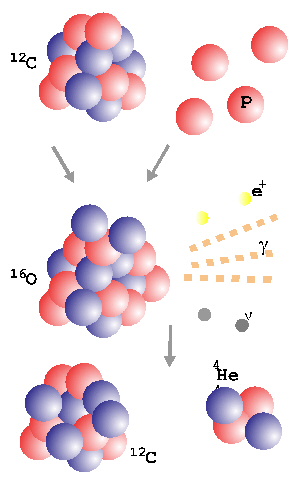
Simplified picture of the Carbon-Nitrogen-Oxygen
fusion cycle
University of Oregon
The Carbon-Nitrogen-Oxygen Fusion Cycle
When the temperature of the core of a star reaches about 16 million
kelvins
the production of Helium occurs through another fusion cycle,
called the Carbon-Nitrogen-Oxygen (CNO) cycle. Here Carbon acts as
a catalyst, it participates in the reaction but it is not "burned".
The cycle involves a total of four protons that react one after the
other with the heavy nucleus (Carbon first). After the first reaction
Carbon is turned into Nitrogen, then Oxygen is produced that finally
decays back into Carbon emitting an alpha particle (Helium
nucleus). During the cycle two neutrinos, three photons and two
antielectrons are also emitted. The antielectrons will annihilate with
electrons producing two more photons.
You might also be interested in:
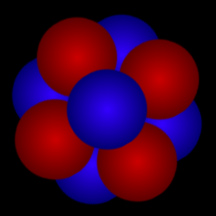
Atoms are composed of a massive, central nucleus surrounded by a swarm of fast-moving electrons. The nucleus is made up of protons and, in most cases, neutrons. Almost all of the mass (more than 99%) of
...more
Fusion in the core of the stars is achieved when the density and temperature arising from the gravitational pressure are high enough. There are different fusion cycles that occur in different phases of
...more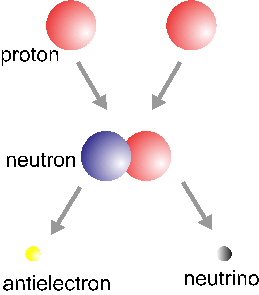
The basic Hydrogen fusion cycle involves four Hydrogen nuclei (protons) and two electrons and yields a Helium nucleus, two neutrinos and six photons. This process occurs in three steps: the first one is
...more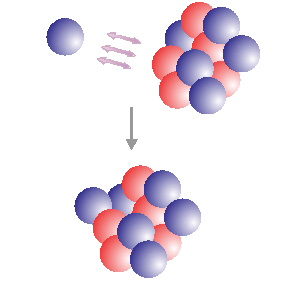
Neutron capture can occur when a neutron approaches a nucleus close enough for nuclear forces to be effective. The neutron is captured and forms a heavier isotope of the capturing element. When the new
...more
A Supernova is a very massive star that explodes at the end of its life cycle. The supernova is the furnace where the heavy elements (heavier than iron) are formed by neutron capture.
...more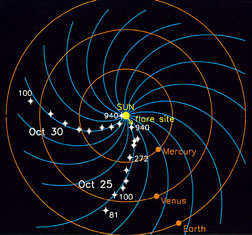
IMF stands for Interplanetary Magnetic Field. It is another name for the Sun's magnetic field. The Sun's magnetic field is enormous and is carried by the solar wind. The solar wind and magnetic field are
...more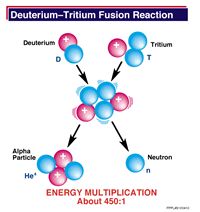
Nuclear fusion is a process where two or more nuclei combine to form an element with a higher atomic number (more protons in the nucleus). Fusion is the reverse process of nuclear fission. Fusion of light
...more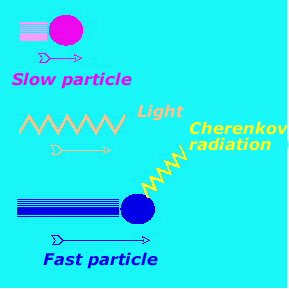
The theory of relativity states that no particle can travel at the speed of light in a vacuum. However, light travels at lower speeds in dense media, like water. A particle traveling in water must have
...more