Voyager
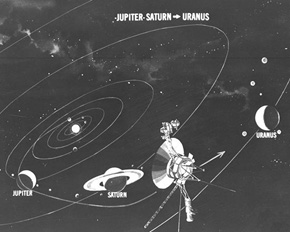
The rare arrangement of planets Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune in the 1980's made it possible for the Voyager spacecrafts to visit them over a 12 year span instead of the normal 30. They used gravity assists to swing from one planet to the next, conserving fuel.
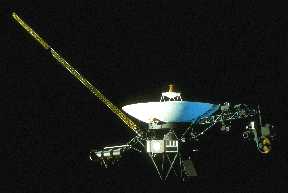
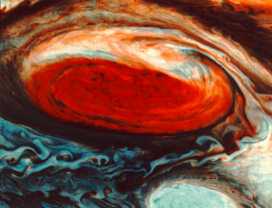
Voyager 2 was launched on Aug. 20, 1977, followed by Voyager 1 on Sep. 5. Both encountered Jupiter in 1979, returning photographs and information on its many moons. Scientists learned that Jupiter's Great Red Spot is really a complex storm, and that Io, one of Jupiter's moons, has active volcanism. These volcanoes are caused by extreme tidal bulges, due to the gravitational pull of Jupiter and its other moons on Io.
Voyagers 1 and 2 then continued to Saturn, with Voyager 1 arriving in November 1980 and Voyager 2 in August 1981, where they studied the true composition of Titan's atmosphere, believed to be similar to Earth's ancient environment. They also learned that Saturn's rings formed from particles broken off its moons by comets and meteors.
Voyager 2 then headed for Uranus and Neptune. It gave us our first close-range look at the two planets, finding an unusually shaped magnetic field around Uranus, caused by the tilt of that planet's axis. Voyager 2 later learned that the strongest winds in our solar system exist on Neptune, and that Neptune's Great Dark Spot is really a hole in its atmosphere.
The Voyager missions discovered a total of 21 new moons and returned information that has changed the field of space science. The two spacecrafts have almost reached the boundary of our solar system called the heliopause. They will continue transmitting for another 20 years until their nuclear generators no longer supply adequate energy.