Albert Einstein developed the two parts of the theory of relativity between 1905 and 1915.
Click on image for full size
Courtesy of Tracey Keifer. Emilio Segre Visual Archives. American Institute of Physics.
The Theory of Relativity
Albert Einstein developed one of the most famous theories in the history of science, the theory of relativity. This theory actually has two parts: the special theory of relativity and the general theory of relativity. These two theories introduced some very new, different, and strange ideas about the basic nature of the Universe.
According to special relativity, very odd things happen when an object moves at nearly the speed of light. Time slows down, the length of an object becomes shorter, and the mass of the moving object increases. If two observers are moving relative to each other, they may disagree as to whether two events happen at the same time. Mass and energy can be converted back and forth according to Einstein's famous equation, E = mc2. Einstein introduced the special theory of relativity in 1905.
The general theory of relativity claims that the "shape" of space itself can be curved near large objects that have a lot of gravity. In fact, according to relativity, gravity isn't so much a force as a curvature of space. Even rays of light curve when they pass through the space near a massive object. This is why black holes can "suck up" light that passes near them. Einstein developed the general theory of relativity between the years of 1907 through 1915.
You might also be interested in:

Scientists use the word theory differently than nonscientists. "It’s just a theory," you hear people say. When speaking casually, people often use the word "theory" to mean a "guess" or a "feeling". In
...more
Some basic concepts find applications in many, many places throughout science, especially physical science. We have grouped these "starting points for science" into three clusters: space, time, and matter.
...more
Astronomers have discovered an extrasolar planet only three times more massive than our own, the smallest yet observed orbiting a normal star. The star itself is not large, perhaps as little as one twentieth
...more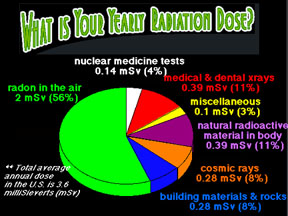
Radiation comes in two basic types: electromagnetic radiation transmitted by photons, and particle radiation consisting of electrons, protons, alpha particles, and so forth. Electromagnetic radiation,
...more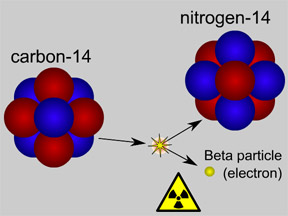
Carbon-14 dating (also called "radiocarbon dating") is used to determine the age of materials that contain carbon that was originally in living things. It is often used in archeology and some
...more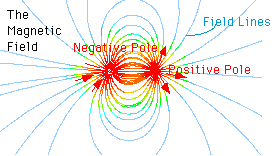
The force of magnetism causes material to point along the direction the magnetic force points. This property implies that the force of magnetism has a direction. As shown in the diagram to the left, the
...more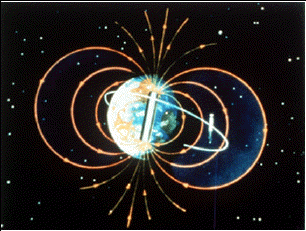
The Earth is a good example of a planetary dipole, where the lines of force point in a direction out of the South (magnetic) Pole and into the North (magnetic) Pole. Planets can also show evidence of quadrupoles
...more















