This image shows the region on Mars in the vicinity of Gusev Crater. The left part of the image is a grayscale "photo" of the area. The right-hand part of the picture is color-coded to indicate elevations; green represents low places, orange and red indicate higher elevations. The central image is a global view of Mars, centered on 180° W longitude, with the location of Gusev Crater marked. For reference, Gusev Crater is roughly 130 km (81 miles) across; Mars is about 6,794 km (4,222 miles) in diameter.
Click on image for full size
Images courtesy NASA.
Gusev Crater location on Mars
Gusev Crater is an impact crater on Mars that
looks as though a lake may have once filled it in the distant past. One
of the two Mars
Exploration Rovers (MER) will explore Gusev Crater beginning in January
2004.
Gusev Crater is about 145 km (90 miles) wide and covers an area roughly
the size of the state of Connecticut. It is located at 14.6° South
latitude and 175.3° East longitude, along the boundary between Mars'
southern highlands and
its lowland
northern plains. The crater is about
3,000 km (1,900 miles) southeast of the volcano Elysium Mons. Scientists
believe the Gusev Crater was formed by the impact of an asteroid three
to four billion years ago.
A valley named Ma'adim Vallis, which is connected
to the south side of the crater, looks like it may have been a river
channel that poured water into
the crater in the past, forming a large lake. If the crater was indeed
a lake, scientists expect it to contain layers
of sediments as much as 915 meters (3,000 feet) thick that flowed in with the water. There may
be other clues to a watery past within the crater, such as deposits
of minerals, such as halite and gypsum,
that form when water evaporates. Wet environments are the best places to look for life,
which is why scientists are so eager to track down places on Mars that were once wet.
The MER
robot Spirit is slated to land somewhere within an
81 km by 12 km (50 by 7 miles) oval
near the center of Gusev Crater. Once settled into its new "home", Spirit will begin its mission of
exploring for geologic evidence of the presence of water in Gusev Crater's past.
You might also be interested in:

Minerals occur naturally on rocky planets and form the building blocks of rocks. They are non-living, solid, and, like all matter, are made of atoms of elements. There are many different types of minerals
...more
What’s that on your chips? It’s a mineral called halite! If you look closely at ordinary table salt, you will see that, just like other minerals, it looks like crystals. Halite is salt. In its natural
...more
You can find gypsum in sedimentary rocks, deserts, and caves. Large amounts can form in layers on a salty sea or lake bottom when water evaporates leaving the mineral behind. Gypsum sometimes forms when
...more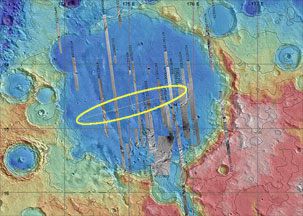
The first of two Mars Exploration Rovers (MER) landed within Gusev Crater on Mars on January 3, 2004. The robotic rover, named Spirit, bounced to a halt within an 81 km by 12 km (50 by 7 miles) target
...more
The Martian South Pole was first imaged by Mariner 7. The south polar region is part of the highlands of Mars, consisting of old, cratered terrain, and other interesting geologic features. The Mariner
...more
Isidis Planitia is flat plain within an ancient impact crater on the surface of Mars. Isidis Planitia is about 1500 km (930 miles) across. It is just north of the Martian equator near the center of the
...more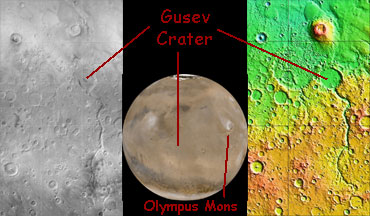
Gusev Crater is an impact crater on Mars that looks as though a lake may have once filled it in the distant past. One of the two Mars Exploration Rovers (MER) will explore Gusev Crater beginning in January
...more














