This image shows the rock Yogi and tracks from the Rover.
Click on image for full size
Courtesy of NASA
Weathering processes on Mars
Unlike the rocks of Earth, where there are many things which cause erosion, the rocks of Mars erode because of only two things: wind and acid fog.
Acid fog is very important, but because there is not a lot of water, the action of sand and wind is the most important thing to cause changes to the planet's surface.
Sand and dust from the surface is whipped up by the winds of Mars and distributed around the globe in global dust storms. The force of winds during these storms pounds sand into the rocks and breaks them down.
During the Mars Pathfinder mission, scientists found things which pointed to the importance of wind erosion:
A wind tail is shown behind the rock "
Yogi" in the picture to the left.
You might also be interested in:

Sand grains on Earth are usually made of quartz. Sand grains of Mars seem to come from basalt. They seem to be particles which are cemented together, rather than round crystal fragments such as sand grains
...more
People were really excited when Pathfinder landed on Mars on July 4, 1997. The Mars Pathfinder mission (MPF for short!) was sent to Mars to look at the rocks and soil of Mars. The MPF was actually 2 parts,
...more
This image shows pits and holes in a small rock found by the Mars Pathfinder Rover. The Souffle rock also reveals a very pitted surface. These pits and holes are the result of sand caught up in the winds
...more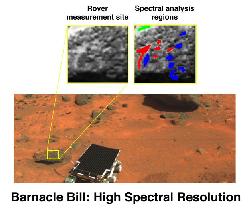
The rocks explored by the Mars Pathfinder's Rover are classified into two groups according to how they eroded. Rocks put in place as a result of an impact which forms a crater are usually much less eroded
...more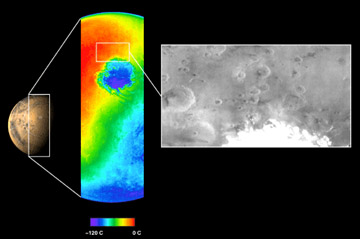
The Mars Odyssey was launched April 7, 2001. After a six-month journey, the Odyssey arrived at Mars on October 24, 2001. The instruments onboard the Mars Odyssey will study the minerals on the surface
...more
The Mars 2005 mission is still in the planning stages. It is set to launch in the year 2005.
...more
Aerobraking slowed the Mars Global Surveyor down when it reached Mars. Aerobraking also helped MGS to get into the right orbit for mapping the surface of Mars. Aerobraking means that the MGS flew through
...more















