Galileo image of Gaspra
(29 October 1991)
Click on image for full size
NASA/JPL
Asteroids
Asteroids are small bodies that are believed to be left over from the beginning of the solar system 4,600 million years ago. They are rocky objects with strange shapes up to several hundred km across, but most are much smaller.
Many thousands of asteroids lie in a belt between Mars and Jupiter. Scientists think that this debris may be the remains of an early planet, which broke up early in the solar system. Several thousand of the largest asteroids in this belt have been given names.
You might also be interested in:

Anthony Wesley is an astronomer in Australia. One night in July 2009, Wesley noticed a dark spot on Jupiter that hadn't been there before. He had discovered the remains of a huge impact on Jupiter! A comet
...more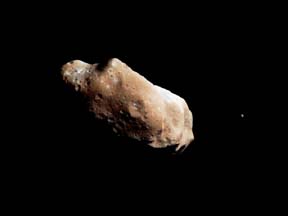
Scientists found a satellite orbiting the asteroid, Eugenia. This is the second one ever! A special telescope allows scientists to look through Earth's atmosphere. The first satellite found was Dactyl.
...more
NASA is going to send a spacecraft to visit an asteroid. Two countries will work on the space mission - Japan and the United States. The name of the asteroid is Nereus. Nereus is a small asteroid. It is
...more
Did you know that asteroids can crash into the Earth? Don't worry, it probably won't happen, but there is a chance. So scientists are watching as many asteroids as they can, just in case one heads to
...more
Lutetia is a medium-sized asteroid. It orbits the Sun in the main asteroid belt. The asteroid belt is between the planets Mars and Jupiter. Lutetia was discovered by Hermann Goldschmidt in Paris in 1852.
...more
Did we come from Mars? Scientists say that tons of rocks came to Earth from Mars many years ago. These rocks broke off of Mars when asteroids ran into it. They say that tiny organisms called microbes
...more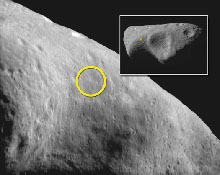
The NEAR spacecraft has been in orbit around the asteroid Eros since Valentine's Day of last year. That was the first time a spacecraft ever orbited an asteroid! Now NEAR will attempt another first --
...more















