This is an image of Io.
Click on image for full size
The Jet Propulsion Laboratory
Io's Atmosphere
There are no clouds and lightning. Io has a very important atmosphere, even though it is very thin and it does not stay on Io for very long.
Io's atmosphere comes from its volcanoes, then fades away. Because the atmosphere comes from it's volcanos, the air of Io is made primarily of sulphur.
Once the particles from the atmosphere get into the magnetosphere, they create a donut-shaped cloud of material around Io.
The Galileo spacecraft, in exploring the moons of Jupiter will try to learn more about the atmosphere of Io.
You might also be interested in:
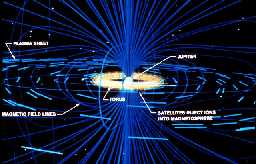
A satellite which has an atmosphere, such as Jupiter's moon Io will leave a cloud of particles behind as it orbits the planet. This cloud of particles is called a torus. The torus is shown in yellow in
...more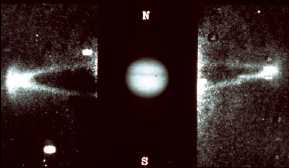
A satellite which has an atmosphere, such as Jupiter's moon Io, and which also is inside a magnetosphere (unlike the Earth's moon), will leave a cloud of particles behind as it orbits the planet. This
...more
Most forms of life leave behind signs that they are there. Plants help make oxygen and some creatures help make nitrogen. People leave behind smog, television signals, and garbage. Scientists find life
...more
Amalthea was discovered by E Barnard in 1872. Of the 17 moons it is the 3rd closest to Jupiter. Amalthea is about the size of a county or small state. Amalthea is named after the goat in Greek mythology
...more
Callisto was first discovered by Galileo in 1610. It is the 2nd largest moon in the solar system, and is larger than the Earth's moon. It is about as big as the distance across the United States. Callisto
...more
Measurements by the Galileo spacecraft have been shown that Callisto is the same inside from the center to the surface. This means that Callisto does not have a core at the center. This means that, unlike
...more
Many different types of surface are shown in this picture. In the front is a huge crater, which goes for a long way over the surface. This crater could be compared to that of Mimas. They both show that
...more














