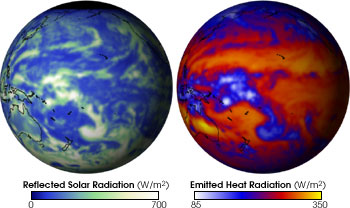
Earth's energy is out of balance: more is absorbed from the sun than emitted back to space.
Courtesy of NASA
“Missing” Heat May Affect Future Climate Change
Scientists know that more of the Sun’s energy gets to our planet than leaves. It hasn’t always been this way. More energy is sticking around as heat because there are more heat-trapping greenhouse gases in the air than there used to be. That’s causing global warming.
Where does the energy go? Scientists would like to know. They have been looking for heat energy in the atmosphere and ocean using satellites, ocean floats, and other instruments. But they can’t seem to find all the heat. In fact, they can only find about half of it. If the energy came to Earth and has not left, then it must be around here somewhere, but where?
Lots of heat might be lurking in places that we can’t watch with satellites or other instruments. The deep ocean is one of those places. Scientists have found warmer ocean water as much as 6,500 feet deep in the ocean (about 2,000 meters). There may be more heat even deeper in the ocean, but we don’t have a way to measure it.
It is important to measure where energy goes on Earth so that we can understand how climate is changing. Scientists are hoping that when we invent new ways to measure heat in the deep ocean and other places, we will be able to solve the mystery of the missing heat.
Last modified May 21, 2010 by Lisa Gardiner.
You might also be interested in:

Only a tiny amount of the gases in Earth’s atmosphere are greenhouse gases. But they have a huge effect on climate. There are several different types of greenhouse gases, but they all have something in
...more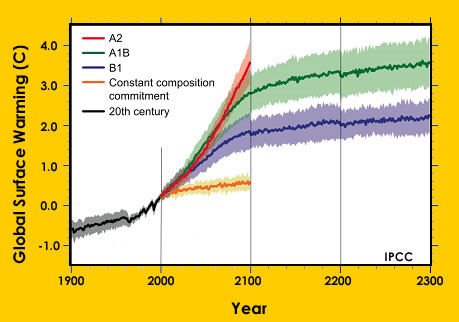
Earth’s climate is getting warmer. During the past 100 years Earth’s average temperature rose about 0.6° Celsius (1.0° F). Things that people are doing like burning fossil fuels, changing the way land
...more
Scientists have learned that Mount Hood, Oregon's tallest mountain, has erupted in the past due to the mixing of two different types of magma. Adam Kent, a geologist at Oregon State University, says this
...more
The Earth's mantle is a rocky, solid shell that is between the Earth's crust and the outer core. The mantle is made up of many different reservoirs that have different chemical compositions. Scientists
...more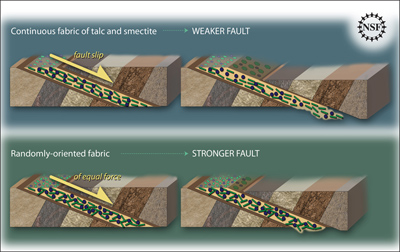
Some faults look strong and like they wouldn’t cause an earthquake. But it turns out that they can slip and slide like weak faults causing earthquakes. Scientists have been looking at one of these faults
...more
The sun goes through cycles that last approximately 11 years. These solar cycle include phases with more magnetic activity, sunspots, and solar flares. They also include phases with less activity. The
...more
Studying tree rings doesn't only tell us the age of that tree. Tree rings also show what climate was like while the tree was alive. This means that tree rings can tell us about climates of the past. Two
...more