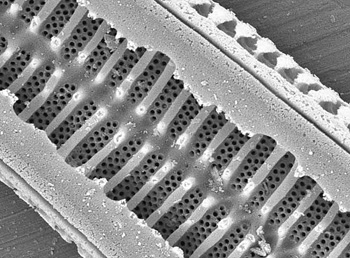
Image of the diatom, Stenopterobia curvula.
Click on image for full size
Courtesy of Peter Siver, Connecticut College
Searching for Tiny Fossils
News story originally written on January 7, 2009
Not all fossils are the size of dinosaurs. Some are very small, so small that you need a powerful microscope to find them.
Scientist Peter Siver has been looking for very small fossils for 20 years. He studies creatures called diatoms and has found them all over North America. He has discovered 60 species. Some of the diatoms that he studies are fossils found in rocks and mud and others are living today in lakes and the ocean. Usually, they are so small that you can’t see them without a microscope. Each diatom is made of just a single cell.
Fossil diatoms may be small, but what they can tell us about the climate can be huge. Peter Siver found fossil diatoms in 48 million years old rocks in the cold Arctic tundra of Canada. He discovered they were the same type of diatom that today live in the tropics. So, these tiny fossils tell us that that the chilly Arctic used to be quite warm 48 million years ago.
Last modified March 6, 2009 by Lisa Gardiner.
You might also be interested in:

Fossils are evidence of what life was like long ago. The oldest fossils are over three billion years old and the youngest fossils are about 10,000 years old. Scientists that study fossils know that creatures
...more
It is too cold for trees to grow in the north polar region. This place without trees is called the Arctic tundra. Trees can not grow there but many other things can! During the summer, grass, flowers,
...more
Members of the Kingdom Protista are an unusual group of organisms that were put together because they don't really seem to belong to any other group. Some protists look or act like plants, others look
...more
Scientists have learned that Mount Hood, Oregon's tallest mountain, has erupted in the past due to the mixing of two different types of magma. Adam Kent, a geologist at Oregon State University, says this
...more
The Earth's mantle is a rocky, solid shell that is between the Earth's crust and the outer core. The mantle is made up of many different reservoirs that have different chemical compositions. Scientists
...more
Some faults look strong and like they wouldn’t cause an earthquake. But it turns out that they can slip and slide like weak faults causing earthquakes. Scientists have been looking at one of these faults
...more
The sun goes through cycles that last approximately 11 years. These solar cycle include phases with more magnetic activity, sunspots, and solar flares. They also include phases with less activity. The
...more