The JOIDES Resolution will venture into the Pacific on its first expedition since it was refurbished.
Click on image for full size
Image Courtesy of the National Science Foundation
Scientists to Investigate Role of Equatorial Pacific Ocean in Global Climate System
News story originally written on February 23, 2009
A team of scientists is out in the Pacific Ocean by the equator in order to collect sediment cores from the ocean floor. The sediment cores contain information about the Earth's past climate that will help the scientists determine what the climate will be like in the future.
The equatorial Pacific is a complicated region that affects the Earth's climate in many ways. The Sun warms the ocean here, this is one of the main regions where carbon dioxide transfers from the deep ocean to the atmosphere.
Over the last 55 million years, the global climate has gone through different periods of being extremely warm and extremely cold. Information on these past climates is contained in sediments on the ocean floor, and information scientists get from this expedition will help them understand how the Earth has become so warm and cold in the past.
You might also be interested in:

To figure out what the Earth might be like in the future, scientists need to know how Earth reacts to changes. Models help scientists to better understand how the Earth works and how it will react to climate
...more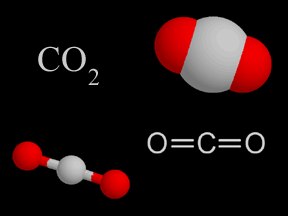
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a kind of gas. There isn't that much carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, but it is still very important. Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas. That means it helps trap heat coming
...more
Scientists have learned that Mount Hood, Oregon's tallest mountain, has erupted in the past due to the mixing of two different types of magma. Adam Kent, a geologist at Oregon State University, says this
...more
The Earth's mantle is a rocky, solid shell that is between the Earth's crust and the outer core. The mantle is made up of many different reservoirs that have different chemical compositions. Scientists
...more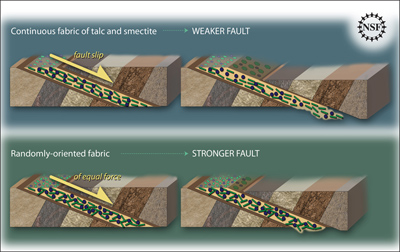
Some faults look strong and like they wouldn’t cause an earthquake. But it turns out that they can slip and slide like weak faults causing earthquakes. Scientists have been looking at one of these faults
...more
The sun goes through cycles that last approximately 11 years. These solar cycle include phases with more magnetic activity, sunspots, and solar flares. They also include phases with less activity. The
...more
Studying tree rings doesn't only tell us the age of that tree. Tree rings also show what climate was like while the tree was alive. This means that tree rings can tell us about climates of the past. Two
...more















