At a coastal upwelling zone, wind blow parallel to a coast, water at the ocean surface moves away from the coast and deep water rises up to take its place.
Courtesy of NOAA
Ocean Upwelling
There are places in the ocean where water from the deep sea travels up to the surface. These are called areas of upwelling. The deep waters can have a large influence upon life in the ocean and the climate too.
Upwelling often happens where wind blows along a coastline. The wind causes the water at the ocean surface to move perpendicular to it, away from the coast, because of a process called Ekman transport. When surface water moves away from the coast, water from deeper in the ocean rises up and takes its place.
The water that is moved up to the surface is usually cold and rich in nutrients, which come from the rotting bodies of dead sea creatures that sunk into deep water. When the deep water gets to the surface, these extra nutrients are snatched up by plankton that floats in the ocean. The number of plankton grows where there is upwelling. Tiny animals gobble up the plankton and fish eat the tiny animals. This means that upwelling areas are full of marine life. About half the fish caught in the world comes from places where there is upwelling.
Upwelling also happens as a part of El Niño (ENSO) events in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of Ecuador and Peru. This has an impact on weather, changing the pattern of precipitation in many areas of the world.
Downwelling is the opposite of upwelling - surface waters pushing down into deeper areas of the ocean. This happens when winds cause Ekman transport to push water toward a coast and then deeper in the ocean.
Last modified September 18, 2008 by Lisa Gardiner.
You might also be interested in:

Wind is moving air. Warm air rises, and cool air comes in to take its place. This movement creates different pressures in the atmosphere which creates the winds around the globe. Since the Earth spins,
...more
If you like anchovies on your pizza, there is a good chance that the little fish now swimming in tomato sauce was once swimming in the Southeast Pacific Ocean. It was probably caught off the coasts of
...more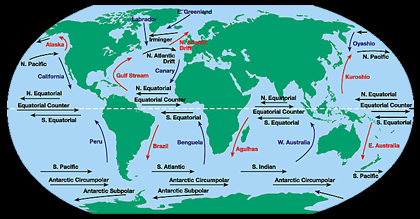
The water at the ocean surface is moved primarily by winds that blow in certain patterns because of the Earth’s spin and the Coriolis Effect. Winds are able to move the top 400 meters of the ocean creating
...more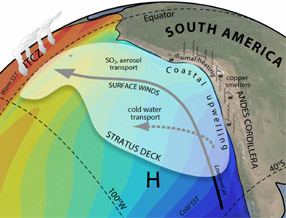
The winds in the Southeast Pacific mainly blow from south to north. They have a strong effect on the climate in the region and worldwide. The winds in this area get their start with a major flow in the
...more
There are many connections between the ocean and the atmosphere in the Southeast Pacific Ocean. Strong winds blow north along the coast of South America. These winds stir up the ocean. That brings cold
...more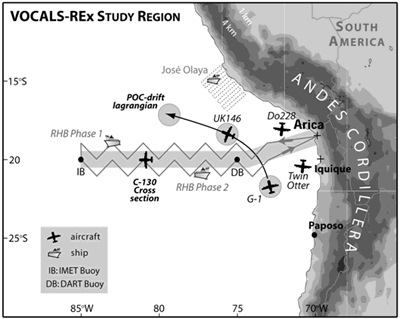
Scientists must work very hard to understand the data collected in field campaigns like VOCALS. They must review and study it to determine what has been learned. Many model runs will be made and analyzed.
...more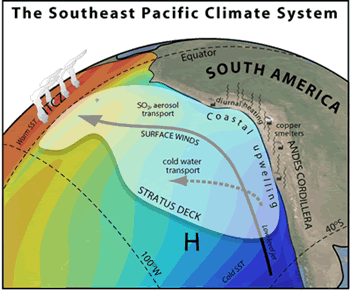
The Southeast Pacific Ocean region off the coastal areas of Peru and Chile is one part of the world where stratus and stratocumulus clouds are frequently present. Other areas include the subtropical climate
...more














