Click on image for full size
Image courtesy of NOAA, photograph by Captain Robert A. Pawlowski.
Ocean Chemistry
The oceans are full of water. Ocean water is not just pure water, though. Ocean water has many different chemicals in it, especially salt.
The salt in sea water is a lot like the salt we sprinkle on food. Sea salt has other chemicals in it too. The main other chemicals in sea salt are magnesium, sulfate, calcium, and potassium.
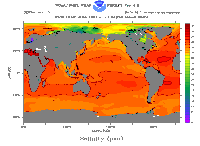
Why is the ocean salty? When it rains on land, some of the water dissolves minerals in rocks. That water flows in rivers to the sea. It carries the minerals with it. When the water evaporates back out of the ocean, it leaves the minerals behind. The minerals make sea water salty.
Some parts of the ocean have more salt than others. For example, melting glaciers dump lots of fresh water into the ocean. Places in the ocean near melting glaciers aren't as salty as the rest of the ocean.
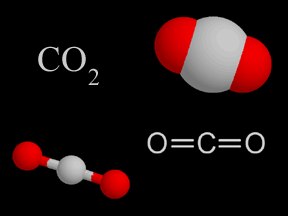
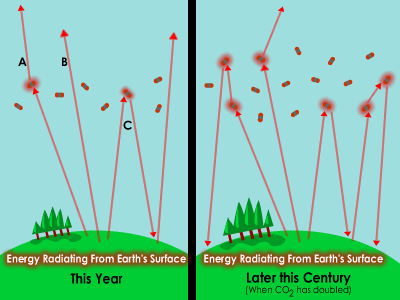
Some gases are dissolved in sea water too. There is carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere dissolved in sea water. That is important because carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas. Scientists want to know how much carbon dioxide the oceans can hold. It will help them predict climate change. When carbon dioxide dissolves in water, it makes an acid. Too much acid can harm corals, shellfish, and other creatures that live in the seas.
People and other living things can also change the chemistry of the oceans. If farmers use too much fertilizer, some of it gets washed into rivers. The rivers carry the fertilizers to the sea. Some tiny creatures in the ocean love the nitrogen from the fertilizer and grow like crazy. As they grow, they use up lots of oxygen. When large areas of the ocean lose oxygen, fish and crabs and other animals die.