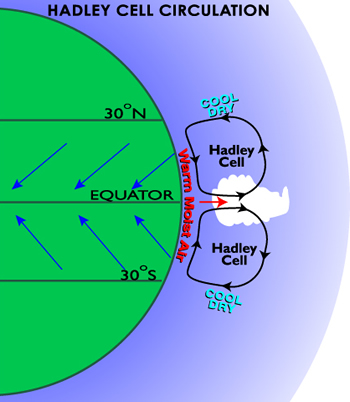
The Hadley Cell involves air rising near the equator, flowing toward the North and South Poles, returning to the surface of the Earth in the subtropics, and flowing back toward the equator at the surface of the Earth. This produces winds called the trade winds and the tropical easterlies.
Click on image for full size
Image courtesy of Tinka Sloss
Hadley Cell
The Hadley cell is an atmospheric circulation pattern in the tropics that produces winds called the tropical easterlies and the trade winds. In the Hadley cell, air rises up into the atmosphere at or near the equator, flows toward the poles above the surface of the Earth, returns to the Earth’s surface in the subtropics, and flows back towards the equator.
This flow of air occurs because the Sun heats air at the Earth’s surface near the equator. The warm air rises, creating a band of low pressure at the equator. Once the rising air reaches the top of the troposphere at approximately 10-15 kilometers above the Earth’s surface, the air flows toward the north and south poles. The Hadley cell eventually returns air to the surface of the Earth in the subtropics, near 30 degrees north or south latitude.
Air near the surface flows toward the equator into the low pressure area, replacing the rising air. This area of low pressure and converging winds (air flowing together) is called the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ). These winds are turned toward the west by the Coriolis effect and become the trade winds or the tropical easterlies.
The air that returns back to the surface of the Earth in the subtropics produces a band of high pressure called the subtropical high. Once the air reaches the surface, some air flows toward the equator from the subtropical high to the lower pressure in the ITCZ to become part of the trade winds.
You might also be interested in:

Wind is moving air. Warm air rises, and cool air comes in to take its place. This movement creates different pressures in the atmosphere which creates the winds around the globe. Since the Earth spins,
...more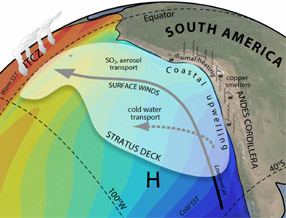
The winds in the Southeast Pacific mainly blow from south to north. They have a strong effect on the climate in the region and worldwide. The winds in this area get their start with a major flow in the
...more
The Atacama Desert is one of the driest places on Earth. The Atacama is in the country of Chile in South America. In an average year, much of this desert gets less than 1 millimeter (0.04 inch) of rain!
...more
The climate at a given location on Earth is the regional climate. Regional climate depends on the temperature, precipitation, and winds experienced over the long term at that location. These characteristics
...more
Rainbows appear in the sky when there is bright sunlight and rain. Sunlight is known as visible or white light and is actually a mixture of colors. Rainbows result from the refraction and reflection of
...more
The Earth travels around the sun one full time per year. During this year, the seasons change depending on the amount of sunlight reaching the surface and the Earth's tilt as it revolves around the sun.
...more
Scientists sometimes travel in specially outfitted airplanes in order to gather data about atmospheric conditions. These research aircraft have special inlet ports that bring air from the outside into
...more