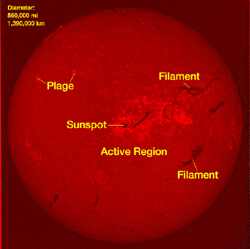
This image shows an active region of the Sun. The National Solar Observatory, Sacramento Park, CA, made it using a special telescope. This image shows plage, areas of brightness and filaments, gas clouds above the Sun’s surface. NSO uses pictures of the Sun like this to help forecast spaceweather.
Click on image for full size
Image courtesy of the National Solar Observatory at Sacramento Peak
The Chromosphere
Above the photosphere is the chromosphere,
a region about 2500 kilometers thick. Just prior to and just after
the peak of a total solar eclipse ,
the chromosphere appears as a thin reddish ring. The conspicuous
color of the chromosphere (compared to the mostly white corona)
led to its name (meaning ``color sphere.'')
The chromosphere is most easily viewed in emission
lines such as Hydrogen alpha, where bright regions known
as plages, and dark features called filaments are visible. Filaments
are the name given to prominences
when they are seen on the solar disk.
Spicules are visible in the chromosphere on the limb of the sun.
They are jets of plasma shooting up from supergranule boundaries.
You might also be interested in:

Most of the energy we receive from the Sun is the visible (white) light emitted from the photosphere. The photosphere is one of the coolest regions of the Sun (6000 K), so only a small fraction (0.1%)
...more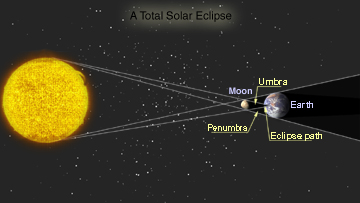
An eclipse of the Sun occurs when the Earth passes through the Moon's shadow. A total eclipse of the Sun takes place only during a new moon, when the Moon is directly between the Sun and the Earth. When
...more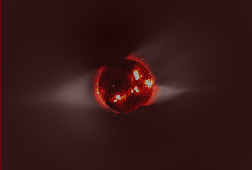
Rising above the Sun's chromosphere , the temperature jumps sharply from a few tens of thousands of kelvins to as much as a few million kelvins in the Sun's outer atmosphere, the solar corona. Understanding
...more
Eclipses have been watched for centuries, but it was only recently that we understood what really occurs. Eclipses have always been fascinating to watch, but they weren't always welcome. For many years,
...more
The gas in the solar corona is at very high temperatures (typically 1-2 million kelvins in most regions) so it is almost completely in a plasma state (made up of charged particles, mostly protons and electrons).
...more
Sunspots are dark, planet-sized regions that appear on the "surface" of the Sun. Sunspots are "dark" because they are colder than the areas around them. A large sunspot might have a temperature of about
...more
Large impressive loop-like structures on the edge of the solar disk sometimes stand out brightly against the dark background of space. Though these structures, called "prominences", appear to be very bright
...more