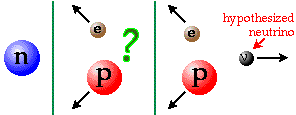The beta decay process: a neutron decays into a proton and an electron
(beta radiation) with the emission of a anti-neutrino
Contemporary Physics Education Project
Related links:
A movie of the beta decay process (467K MPEG) Movie courtesy of University of Oregon
Neutrino History
The "neutrino" was proposed by Wolfgang Pauli in 1930. This particle had to have no electrical charge so Enrico Fermi called this particle "neutrino" which means "little neutral one" in Italian.
Neutrinos don't interact much with matter so they are difficult to detect. In 1956, physicists Reines and Cowan found evidence of neutrinos coming from a nuclear reactor.
You might also be interested in:
The neutrino is an extremely light particle. (You definitely couldn't weigh one on your bathroom scale!) It also has no electric charge. Fusion reactions in the Sun produce neutrinos. By detecting these
...more
All of the matter and energy in the Universe was initially found in a very small space. An explosion happened which caused the Universe to begin expanding.
...more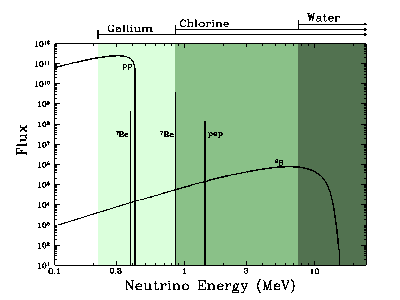
By knowing about fusion inside the Sun, scientists can predict the number of neutrinos that should reach Earth. Experiments on Earth have been set up to detect neutrinos in order to test these predictions.
...more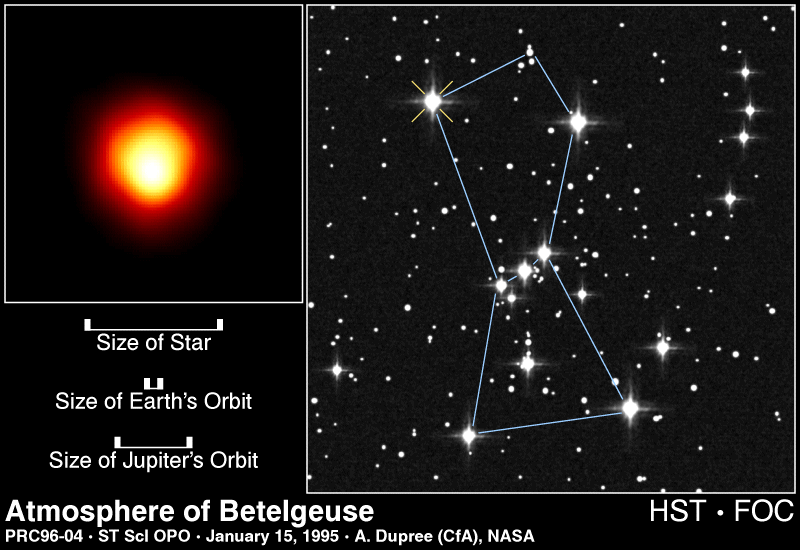
When the temperature in the core of a star is really hot (100 million degrees Kelvin!) fusion of Helium into Carbon happens. Oxygen is also formed when the temperature is this high. When it gets even hotter
...more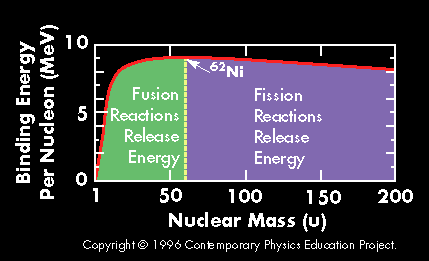
A plot of the binding energy per nucleon vs. atomic mass shows a peak atomic number 56 (Iron). Elements with atomic mass less then 56 release energy if formed as a result of a fusion reaction. Above this
...more
Nuclear fusion has been achieved in a controlled manner (that means no bombs are involved!!). Right now, these fusion experiments take in more energy than they produce. So they can't be used right now
...more
In the Hydrogen bomb, an explosion takes place so that the temperature and density is right for fusion to occur. This fusion results in a sudden release of energy that produces an even bigger explosion.
...more