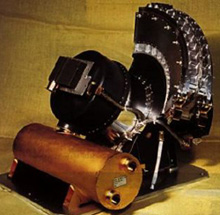
A photo of the SWICS instrument
Click on image for full size
Courtesy of the University of Maryland Space Physics Group
SWICS Instrument Page
The SWICS (Solar Wind Ion Composition Spectrometer) instrument on Ulysses is to measure the frequency of occurence, temperature and average speed of all the major solar wind ions, from Hydrogen through Iron. Another main goal of
the Ulysses mission is to test
the solar wind coming from the poles of the Sun. These regions of the Sun are known to give off high-speed streams (HSST's) of solar wind. Scientists are using the SWICS instrument to see if these streams are of constant speed and constant composition.
The instrument has already collected data at the north and south pole of the Sun. Scientists have already found evidence that speed and composition are steady at the poles of the Sun.
One interesting fact about the SWICS instrument is that it measures the composition, temperature, and speed of solar wind ions of speeds ranging from 175 km/s to 1280 km/s. Compare these to the velocity of Ulysses, the fastest space probe to date travelling at 11.3 km/s!
You might also be interested in:

The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) was one of the most important exploration tools of the past two decades, and will continue to serve as a great resource well into the new millennium. The HST found numerous
...more
Driven by a recent surge in space research, the Apollo program hoped to add to the accomplishments of the Lunar Orbiter and Surveyor missions of the late 1960's. Apollo 11 was the name of the first mission
...more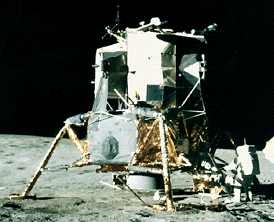
Apollo 12 was launched on Nov. 14, 1969, surviving a lightning strike which temporarily shut down many systems, and arrived at the Moon three days later. Astronauts Charles Conrad and Alan Bean descended
...more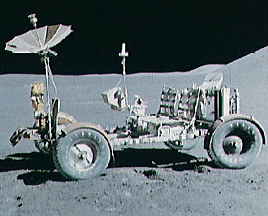
Apollo 15 marked the start of a new series of missions from the Apollo space program, each capable of exploring more lunar terrain than ever before. Launched on July 26, 1971, Apollo 15 reached the Moon
...more
NASA chose Deep Impact to be part of a special series called the Discovery Program on July 7, 1999. The Discovery program specializes in low-cost, scientific projects. In May 2001, Deep Impact was given
...more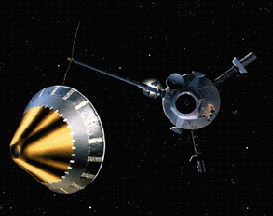
The Galileo spacecraft was launched on October 19, 1989. Galileo had two parts: an orbiter and a descent probe that parachuted into Jupiter's atmosphere. Galileo's main mission was to explore Jupiter and
...more
During 1966 through 1967, five Lunar Orbiter spacecrafts were launched, with the purpose of mapping the Moon's surface in preparation for the Apollo and Surveyor landings. All five missions were successful.
...more