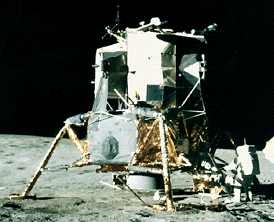
Click on image for full size
Image courtesy of NASA/JPL-Calech/University of Arizona.
Related links:
Phoenix Instruments and Mission Objectives
Animation depicting Phoenix mission (small 3 Mb | large 31 Mb)
Phoenix Mars Lander
The Phoenix Mars Lander is a space mission sent by NASA to the North Polar Region of Mars. Phoenix is searching for and analyzing water ice that scientists believe exists just below the surface of Mars at high northern latitudes. Since water is crucial for the existence of life as we know it, this search for water ice has important implications for the possibility of life on Mars.
Phoenix was launched aboard a Delta rocket from Cape Canaveral in Florida on August 4, 2007. After a 9-month cruise to the Red Planet, Phoenix landed on the northern plains of Mars near the polar ice cap on May 25, 2008. NASA hopes the lander will function for at least 90 sols (Martian days; just over 92 Earth days). The lander uses solar panels to generate electricity, so the onset of winter in the Martian northern hemisphere will eventually deprive the lander of sunlight, ending the mission.
Click here to learn about the instruments onboard the spacecraft and the objectives of the Phoenix mission.
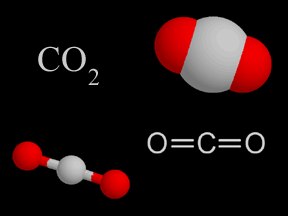
The landing site on Mars is located at 233° East longitude by 68.35° North latitude, a comparable latitude to northern Alaska on Earth. Although diminishing winter sunlight will almost certainly "kill" the lander by preventing it from drawing power from its solar panels, mission scientists hope Phoenix will survive long enough to observe the buildup of ice in its surroundings as the Martian winter sets in. They believe that as much as one meter (3 feet) of dry ice could accumulate in the vicinity of Phoenix, possibly burying the lander under a thick blanket of frozen carbon dioxide!
 Phoenix Instruments and Mission Objectives
Phoenix Instruments and Mission Objectives
 Animation depicting Phoenix mission (small 3 Mb | large 31 Mb)
Animation depicting Phoenix mission (small 3 Mb | large 31 Mb)
 Location of Phoenix landing site on Mars
Location of Phoenix landing site on Mars
 Map of water ice near the Martian North Pole
Map of water ice near the Martian North Pole