An artist's conception of Deep Space 1
Click on image for full size
Image courtesy of NASA
NASA Tests New Technologies with Deep Space 1
NASA launched a spacecraft called Deep Space 1 on October 15, 1998. It tested
some new equipment. During the tests, it flew to a nearby
asteroid called Braille and took pictures of
it.
Deep Space 1 had a new kind of engine. It used xenon gas. (Xenon is like
neon or helium, only heavier.) The engine didn't produce very much
thrust. The force was less then the weight of a piece of paper! But it added up since there isn't any air in space to slow the spacecraft
down. The new engine used ten times less fuel than a normal rocket engine.
Things went so well with Deep Space 1, NASA had it fly by comet Borrelly in September 2001. The Deep Space 1 mission ended on December 18, 2001.
You might also be interested in:

The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is really neat! It was first launched in 1990, but scientists started building it in the 1970's! We have found all kinds of objects like stars, nebulae and galaxies. The
...more
Apollo 11 was the first mission that landed a person on the moon. On July 16, 1969, the U. S. rocket Saturn 5 was launched carrying the lunar landing module Eagle. The Eagle was released and it reached
...more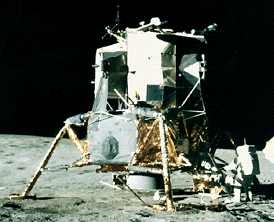
Apollo 12 was launched on Nov. 14, 1969 and arrived at the Moon three days later. Astronauts Charles Conrad and Alan Bean descended to its surface, while Richard Gordon remained in lunar orbit aboard the
...more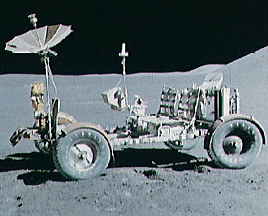
Apollo 15 marked the start of a new series of missions from the Apollo space program, each capable of exploring more lunar terrain than ever before. Launched on July 26, 1971, Apollo 15 reached the Moon
...more
NASA chose Deep Impact to be part of a special series called the Discovery Program. This program is for cheap, scientific projects. In May 2001, NASA said it was ok to start with mission development for
...more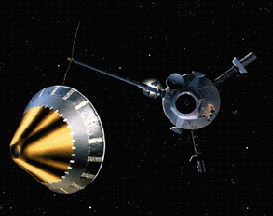
Galileo was a spacecraft that orbited Jupiter for eight years. It made many discoveries about Jupiter and its moons. Galileo was launched in 1989, and reached Jupiter in 1995. The spacecraft had two parts.
...more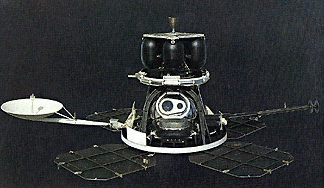
During 1966 through 1967, five Lunar Orbiter spacecrafts were launched, with the purpose of mapping the Moon's surface in preparation for the Apollo and Surveyor landings. All five missions were successful,
...more















