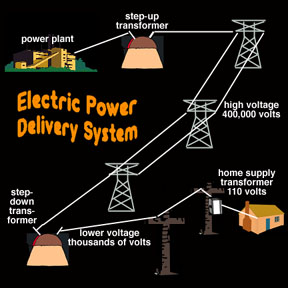
Electrical power travels along transmission wires from power plants to homes and businesses. Along the way, transformers raise or "step up" and lower or "step down" the voltage.
Click on image for full size
Electric Power Delivery System
Electric power supplied to homes and businesses is typically AC (alternating current). The electrons do not travel along the power lines overhead but vibrate back and forth at 60 times per second within these lines. The AC outlet in your home delivers energy not electrons. When you plug in an appliance, the outlet supplies the power to move electrons that are already in the wiring of the appliance, around a closed circuit to produce a current. The energy is supplied to your home as a voltage through a large and very complex power distribution network. After electric power is generated within a power station, it is sent through a network of power lines to consumers. This is done in several steps.
| |
- Electric power leaves the power plant at very high current levels and with voltages of several thousand volts.
- The voltage is "stepped up" (increased) to several hundred thousand volts because less energy is lost during the trip along the overhead power lines at these high voltages.
- Before the power is distributed to industrial users, the voltage is "stepped down" (decreased) to several thousand volts again.
- For home use, the voltage is stepped down even further to 110 volts.
|
Each time the voltage is stepped down, a transformer is used. Transformers are devices that work only with alternating current flows to either step up or step down voltages. They begin to behave badly when direct currents (DC) are superimposed on the normal AC currents that are handled routinely in the power grid. This is the main reason that power grids can be compromised by space weather events.
You might also be interested in:
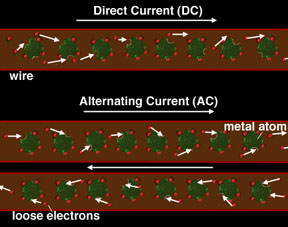
There are two types of electrical currents that can flow through wires: direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC). Direct current (DC) flows in the same direction all the time through an electric
...more
The transformer is not a power source. It functions like a lever to convert a small voltage pushing a large electric current into a large voltage pushing a small electric current or vice versa. The power
...more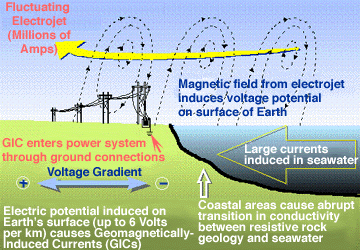
Electric currents in Earth's atmosphere can induce currents in our planet's crust and oceans. Electromagnetic induction works on a grand scale during space weather disturbances. Currents as large as a
...more
Space weather "storms" can cause problems for the systems we use to generate and transmit electrical power here on Earth. In extreme cases, large space weather events can even cause massive blackouts over
...more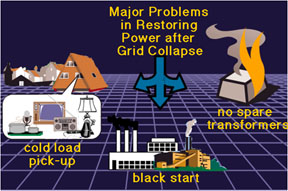
Power grids were not designed to fail completely and be started-up all at once. The basic problem is that it takes energy to produce energy. Hydroelectric, steam and nuclear power plants all require energy
...more
In March 1989 a space weather storm caused the failure of the entire HydroQuebec electrical power system in eastern Canada. Six million people lost electricity for nine or more hours. The blackout of the
...more
Radiation can damage electronic circuits and it can cause electronics to malfunction. Radiation can degrade the semiconductor materials used in electronics, reducing the useful lifetime of the electronics.
...more