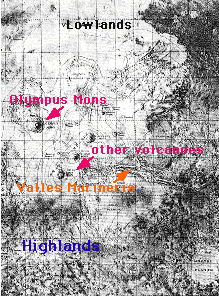
This map shows a portion of the surface of Mars.
Click on image for full size
Image from: NASA
Martian Global Geography
The surface of Mars can be broken into two parts, the highlands and lowlands.
The highlands are in the southern hemisphere (the bottom of the picture). The lowlands are in the northern hemisphere of Mars (top of the picture). The highlands are called that because as a whole, they are much higher than the lowlands.
The highlands are the oldest part of Mars. They have tons of craters. The lowlands are younger. They contain the Tharsis Ridge, where many of the largest volcanoes of Mars are located.
The Mars Global Surveyor mission is taking a lot of measurements about the surface of Mars.
You might also be interested in:

How did life evolve on Earth? The answer to this question can help us understand our past and prepare for our future. Although evolution provides credible and reliable answers, polls show that many people turn away from science, seeking other explanations with which they are more comfortable.
...more
This is an example of the cratered surface of Mars. Almost all of the surface of Mars is covered with craters. Craters can be wiped out over time, so a surface which has many craters is very old. The lowlands
...more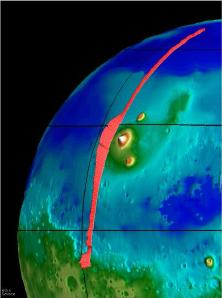
This image, taken from the Mars Global Surveyor mission (MGS), shows the Tharsis Ridge, the green/blue area in the middle of the picture, as well as a portion of the southern hemisphere of Mars. The green
...more
The mission of Mars Global Surveyor (MGS for short) is to map the surface of Mars from space. MGS is also looking at the atmosphere of Mars and the weather of Mars. MGS and the Mars Pathfinder (MPF for
...more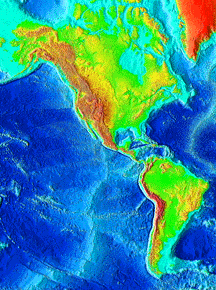
Look at this picture of the surface of the Earth! Can you find these features? the Pacific Ocean floor continents volcanoes mountain ranges volcanic islands faults (Click on the image to see labeled examples
...more
After decades of exploration of Mars, many questions still remain. What happened to the water on Mars? Has all the water escaped is it hidden in the ground and polar caps? What is the present and past
...more
Unlike Earth, there is no continental drift on Mars today. The Martian surface does not seem to have changed or moved in billions of years. 1.) The surface of Mars shows craters at all latitudes and longitudes.
...more
The uniquely red global surface of Mars is marked by many interesting features - some like those on the Earth and others strangely different. The reddish color is caused by rust (iron oxide) in the soil.
...more