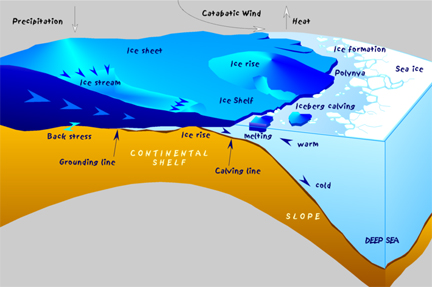
Original Windows to the Universe artwork by Lisa Gardiner using images from NASA.
Geography of Earth's Polar Regions
Location
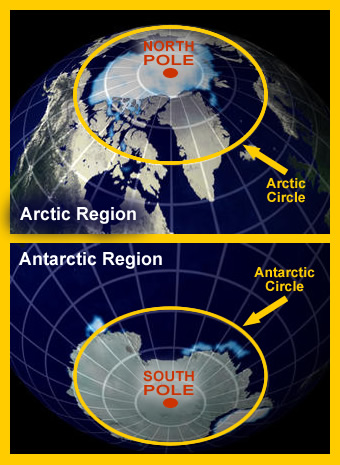
The polar regions are the areas that surround Earth’s geographic North and South Poles. The area surrounding the geographic North Pole is called the Arctic and includes almost the entire Arctic Ocean and northern areas of Europe, Asia, and North America. The area surrounding the geographic South Pole is called the Antarctic and includes the continent of Antarctica and parts of the surrounding Southern Ocean. Earth's geographic poles are in a slightly different location than the magnetic poles.
- The Arctic region extends from the North Pole to the Arctic Circle (66.5°N latitude).
- The Antarctic region extends from the South Pole to the Antarctic Circle (66.5°S latitude).
Day and Night
Because of the tilt of Earth’s axis, the Sun shines for half the year and it is dark for the other half of the year right at the Poles. This makes a year like one long day; the Sun rises in spring, reaches its highest point in the sky in summer, and sets in autumn. So the Sun is only visible only during the warmer months of the year. When the Sun is visible during summer at the South Pole, it is the dark winter months at the North Pole.
At the Arctic and Antarctic Circles there is just one day when the Sun does not set and one day when it does not rise. The Sun does not set on the summer solstice (June 21 in the north and December 21 in the south) and does not rise on the winter solstice (December 21 for the north and June 21 for the south). In the weeks prior to the winter solstice, the number of hours with daylight become fewer and fewer until on the winter solstice day when the Sun does not rise at all for a day. After the winter solstice the amount of daylight increases each day until the summer solstice when the Sun does not set at all for one day.
The time when the Sun is continuously in the sky is called Polar Day. In locations that are between the Arctic Circle and North Pole, or between the Antarctic Circle and South Pole, the length of the Polar Day is between one day and six months long depending on how close the location is to the Pole.