Image courtesy Argonne National Laboratory
Melting Arctic Sea Ice and the Global Ocean Conveyor
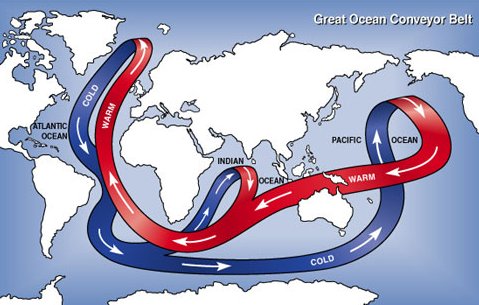
Seawater moves through the Atlantic as part of the Global Ocean Conveyor, the regular pattern by which seawater travels the world’s oceans. The water in the Global Ocean Conveyor circulates because of differences in water density. In the North Atlantic, the differences in water density are mainly caused by differences in temperature. Colder water is denser than warmer water. Water heated near the Equator travels at the surface of the ocean north into cold high latitudes where becomes cooler. As it cools, it becomes denser and sinks to the deep ocean. More warm surface water flows in to take its place, cools, sinks, and the pattern continues.
Melting Arctic sea ice could change this pattern, or halt it altogether.
Recent research shows that Arctic sea ice is melting faster than expected. As the Earth continues to warm and Arctic sea ice melts, the influx of freshwater from the melting ice is making seawater at high latitudes less dense. In fact, data shows that the North Atlantic has become fresher over the past several decades. The less dense water will not be able to sink and circulate through the deep ocean as it does currently. This will disrupt or stop the Global Ocean Conveyor. Scientists estimate that, given the current rate of change, the Global Ocean Conveyor may slow or stop within the next few decades.
Paradoxically, this ocean circulation interference caused by global warming could send Western Europe and North America into a deep freeze. Now the ocean currents carry warmth from the tropics up to the high latitudes. That warmth is lost to the atmosphere keeping the temperatures of places like England, Labrador, and Sweden a bit milder than other places at the same latitude. If the Global Ocean Conveyor were to stop completely, the average temperature of Europe would cool 5 to 10 degrees Celsius.
This would not be the first time that the Global Ocean Conveyor was halted. There is evidence from sedimentary rocks and ice cores that it has shut down several times in the past and those shut downs have caused changes in climate. One of the most pronounced of these, the Younger Dryas Event, happened about 12,700 years ago and temperatures cooled about 5 C in the North Atlantic Region. This may have been a Heinrich event, during which ocean circulation was disrupted when large numbers of icebergs broke off of glaciers and melted in the North Atlantic decreasing the density of the water. Alternatively, ocean circulation may have been disrupted during the Younger Dryas as a large lake of glacial meltwater emptied into the North Atlantic, decreasing salinity rapidly.













