Image courtesy of NASA
Earth's Global Climate
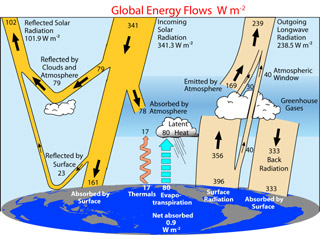
Earth's climate is determined by the amount of energy received from the Sun and the amount of energy held in the Earth system - in short, Earth's radiation budget.
The Sun emits a tremendous amount of energy, in the form of electromagnetic radiation, into space. If we could capture all of that energy and convert it to electricity, we would have more than enough energy to fuel all our needs on this planet, by many time! Most of the Sun's energy flows out of the solar system into interstellar space without ever colliding with anything. A very small fraction of that energy collides with planets, including Earth, before it can escape into interstellar space. This tiny amount of energy from the Sun that Earth intercepts is sufficient to warm our planet and drive its climate system, weather, and support life on Earth.
Earth's distance from the Sun is one of the key factors in determining our climate. We will examine several factors that influence the distance between the Earth and the Sun, and their impact on climate. Another possible factor related to the Sun's influence on climate is the amount of energy emitted from the Sun itself. We will also examine how radiation from the Sun varies with time, and the impact of these variations on climate.
As we will see, if it wasn't for our atmosphere, Earth's climate would be much less pleasant. Thanks to the ability of our atmosphere to retain heat because of greenhouse gases, Earth's temperature is considerably warmer than it would be without an atmophere. So another key factor in determining Earth's climate is the composition of the atmosphere. As the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere has increased, particularly in recent decades, our atmosphere is retaining more and more heat. We will examine the many ways in which the composition of our atmosphere can change, and how it is changing today.
Another factor that impacts the Earth's energy balance is the reflectivity of the Earth - the Earth's albedo. The more reflective the surface - like fresh snow or clouds - the more energy from the Sun is reflected back to space. When surfaces are dark, they absorb solar energy, heating the surface and leading to warming. Because warming leads to melting of ice and snow, a feedback loop develops in which warming leads to more warming, because of the reduction in Earth's reflectivity due to the reduction in ice and snow.