Click on image for full size
Courtesy of NOAA and photographer Captain Albert E. Theberge
Sea Level
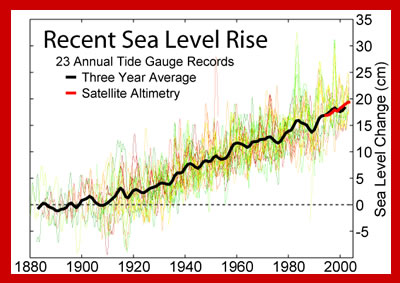
Measuring sea level, the height of the ocean surface, allows scientists to calculate whether sea level is changing over time and how much sea level rise is happening now because of global warming.
But measuring sea level is not easy because the sea is not level. If you tried to draw a flat line at the top of the ocean to mark the sea level you would find that in some places there was water above the line and on other places there was water below the line. This is because of tides and waves. The ocean surface can also bulge upward because of the low atmospheric pressure of a storm.
To even out the differences in sea level caused by waves, scientists use tide gauges. These are containers that block out the waves while measuring sea level. If the information is averaged over a year, then variations like tides are evened out too. This average is called Mean Sea Level.
Satellites are also used to measure sea level. Sea surface height measurements have been recorded from satellites since 1992 by projects of NASA and the French Space Agency.
Some changes in sea level are worldwide, and others happen in one region of the world.
A change in sea level in a region can happen if the level of the ocean has changed with respect to the land. This is called a relative change in sea level. For example, the land that New Orleans, Louisiana (US) is built upon is sinking lower each year, a process called subsidence. Because the land is sinking, the sea level appears to be rising.
When sea level changes worldwide it is called a eustatic change in sea level. This is happening today as global warming melts glaciers and causes seawater to expand , increasing the volume of water in the oceans. In New Orleans, effects of the relative rise in sea level are worsened by eustatic sea level rise due to global warming. Eustatic sea level can also change over geologic time as plate tectonics changes the shape of the oceans and how much water they can hold.