Click on image for full size
Courtesy of COMET program
Ozone in the Stratosphere
About 90% of the ozone in the Earth's atmosphere is found in the region called the stratosphere. This is the atmospheric layer between 16 and 48 kilometers (10 and 30 miles) above the Earth's surface. Ozone forms a kind of layer in the stratosphere, where it is more concentrated than anywhere else.
Ozone and oxygen molecules in the stratosphere absorb ultraviolet light from the Sun, providing a shield that prevents this radiation from passing to the Earth's surface. While both oxygen and ozone together absorb 95 to 99.9% of the Sun's ultraviolet radiation, only ozone effectively absorbs the most energetic ultraviolet light, known as UV-C and UV-B. This ultraviolet light can cause biological damage like skin cancer, tissue damage to eyes and plant tissue damage. The protective role of the ozone layer in the upper atmosphere is so vital that scientists believe life on land probably would not have evolved - and could not exist today - without it.
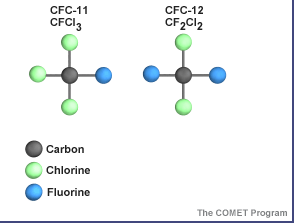
The ozone layer would be quite good at its job of protecting Earth from too much ultraviolet radiation - that is, it would if humans did not contribute to the process. It's now known that ozone is destroyed in the stratosphere and that some human-released chemicals such as CFC’s are speeding up the breakdown of ozone, so that there are "holes" now in our protective shield.
While the stratospheric ozone issue is a serious one, in many ways it can be thought of as an environmental success story. Scientists detected the developing problem, and collected the evidence that convinced governments around the world to take action. Although the elimination of ozone-depleting chemicals from the atmosphere will take decades yet, we have made a strong and positive beginning. For the first time in our species' history, we have tackled a global environmental issue on a global scale.