Click on image for full size
Windows Original (Using images from FAA)
Measuring Atmospheric Pressure
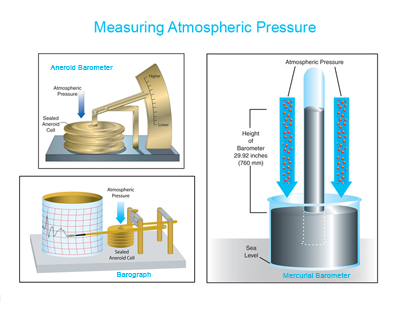
Even though we can't see air, it is real and has pressure. The pressure of the atmosphere changes. It is higher at sea level, and lessens as you go higher up in the atmosphere. Some weather systems have slightly higher pressure than others - you may have heard of High pressure and Low pressure weather systems.Let's look at how atmospheric pressure is measured. For a long time, atmospheric pressure has been measured by a mercury barometer. The first was invented in 1643 by one of Galileo's assistants. A mercurial barometer has a section of mercury exposed to the atmosphere. The atmosphere pushes downward on the mercury (see image). If there is an increase in pressure, it forces the mercury to rise inside the glass tube and a higher measurement is shown. If atmospheric pressure lessens, downward force on the mercury lessens and the height of the mercury inside the tube lowers. A lower measurement would be shown. This type of instrument can be used in a lab or a weather station, but is not easy to move! Measurements from a mercury barometer are usually made in inches of Mercury (in Hg).
An aneroid barometer can be used in place of a mercury barometer. It is easier to move and is often easier to read. This instrument contains sealed wafers that shrink or spread out depending on changes of atmospheric pressure. If atmospheric pressure is higher, the wafers will be squished together. If atmospheric pressure lessens, it allows the wafers to grow bigger. The changes in the wafers move a mechanical arm that shows higher or lower air pressure (see image).
Either a mercury barometer or an aneroid barometer can be set up to make constant measurements of atmospheric pressure. Then it is called a barograph (see image). The barograph may constantly record pressure on paper or foil wrapped around a drum that makes one turn per day, per week, or per month. Nowadays, many mechanical weather instruments have been replaced by electronic instruments that record atmospheric pressure onto a computer.
Atmospheric pressure can be recorded and reported in many different units. This can get a little confusing! As mentioned, a mercury barometer makes measurements in inches of Mercury (in Hg). Pounds per square inch (abbreviated as p.s.i.) is common in the English system of units, and the pascal (abbreviated Pa) is the standard in the Metric (SI) system. Since the pressure exerted by Earth's atmosphere is of great importance, pressure is sometimes expressed in terms of "atmospheres" (abbreviated atm). In weather, the bar and millibar (mb) describe pressure. You'll often hear millibar used by meteorologists when describing low or high pressure weather systems.
In summary, at sea level when it is 0oC,
1 atmosphere = 29.92 in Hg = 14.7 psi = 101,325 Pa = 1,013.25 mb = 1.013 bar