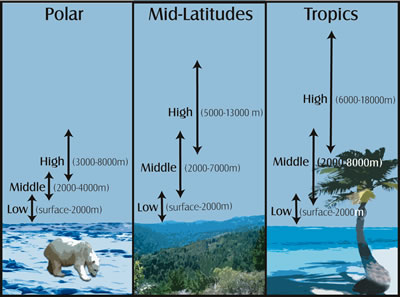
This graphic shows cloud heights at different latitudes on the Earth. For example, a middle cloud like an altocumulus cloud would be found at a lower height in the sky at the poles than at the equator (which is in the tropics).
Courtesy of Lisa Gardiner/UCAR
Cloud Heights at Different Latitudes
Different
types of clouds can be found at different
heights in the sky.
Latitude also plays a role in how high a
cloud is in the sky. Most clouds we see, including clouds that are related to
weather, are located in a layer of the
atmosphere called the
troposphere.
The troposphere has different depths at different places around the Earth. The troposphere is deeper, or higher, near the equator, and it is thinner near the poles. This is because the Sun heats the Earth mostly at and near the equator, and this warm air rises and causes the troposphere to be deeper above this part of the planet. At and near the poles, the air is cooler and sinks, so the troposphere is thinner above this part of the planet. Because of this, high clouds in the tropics have a higher base and a higher top than high clouds in the mid-latitudes or high clouds in the tropics.
You might also be interested in:

Altocumulus clouds are part of the Middle Cloud group. They are grayish-white with one part of the cloud darker than the other. Altocumulus clouds usually form in groups. Altocumulus clouds are about
...more
Altostratus clouds belong to the Middle Cloud group. An altostratus cloud usually covers the whole sky. The cloud looks gray or blue-gray. The sun or moon may shine through an altostratus cloud, but will
...more
Cirrocumulus clouds belong to the High Cloud group. They are small rounded puffs that usually appear in long rows. Cirrocumulus are usually white, but sometimes appear gray. Cirrocumulus clouds are the
...more
Cirrostratus clouds belong to the High Cloud group. They are sheetlike thin clouds that usually cover the entire sky. The sun or moon can shine through cirrostratus clouds. When looking at the sun through
...more
Cirrus clouds are the most common of the High Cloud group. They are made of ice crystals and have long, thin, wispy streamers. Cirrus clouds are usually white and predict fair weather.
...more
Cumulonimbus clouds belong to the Clouds with Vertical Growth group. They are also known as thunderstorm clouds. A cumulonimbus cloud can grow up to 10km high. At this height, high winds make the top
...more
Cumulus clouds belong to the Clouds with Vertical Growth group. They are puffy white or light gray clouds that look like floating cotton balls. Cumulus clouds have sharp outlines and a flat base. Seeing
...more