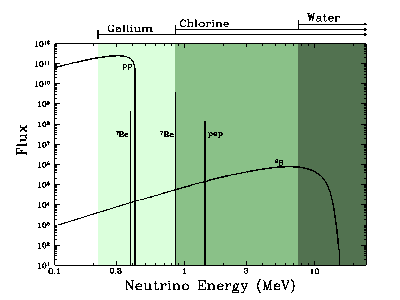
Neutrinos produced in the Sun have different energies. Different types of
detectors are sensitive to different energy ranges.
Image courtesy of John Bahcall, Institute of Advanced Studies
The Solar Neutrino Problem
Theories about
fusion inside the solar core
predict the number of neutrinos
that should reach Earth. Experiments on
Earth have been set up to detect solar neutrinos
in order to test the validity of these models. Current measurements
yield a neutrino flux that is smaller than the theoretical prediction.
The first solar neutrino experiment was performed at the
Homestake mine in South Dakota.
A 600 ton chlorine fluid detector was used and found
a neutrino count about one third of the
theoretical prediction.
The experiment at Kamioka, Japan, found about half
of the predicted neutrino flux. Recent experiments in Russia (SAGE)
and Italy (GALLEX) use Gallium to detect neutrinos and have
found neutrino
fluxes up to 70% of the predicted flux.
Hypothesis that have been formulated to explain the differences between
measurements and theory include the following:
Models of the solar core may need to be refined to improve the prediction
of the neutrino energy spectrum. (Neutrinos produced in the Sun have
different energies and the detectors are sensitive to specific
energy ranges).
There are different types of neutrinos (electron-, muon-, and
tau-neutrinos). Electron neutrinos can be transformed into
muon- and tau-neutrinos, which would not be detected by many of the
present-day experiments. A detector that is sensitive to all
types of neutrinos is presently
under construction in Canada (SNO, Solar
neutrino Observatory).
The interaction between neutrinos and the fluid used in the detectors
may be different than expected.
You might also be interested in:

Fusion in the core of the stars is achieved when the density and temperature arising from the gravitational pressure are high enough. There are different fusion cycles that occur in different phases of
...more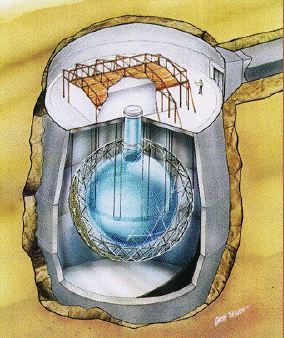
Neutrino interactions with matter are extremely rare, making detection difficult. Neutrino detectors are typically large tanks filled with a fluid that reacts to the passage of neutrinos. To take advantage
...more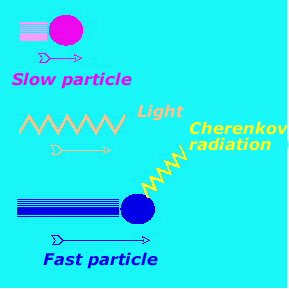
The theory of relativity states that no particle can travel at the speed of light in a vacuum. However, light travels at lower speeds in dense media, like water. A particle traveling in water must have
...more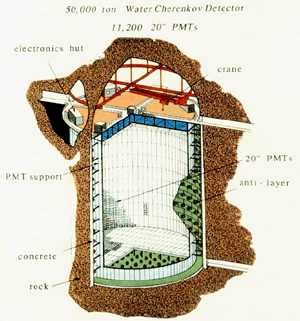
Super-Kamiokande is a water Cerenkov detector located in the Kamioka Mozumi mine in Japan. Its use includes proton decay studies, neutrino detection (from the Sun, the atmosphere and supernovae) and muon
...more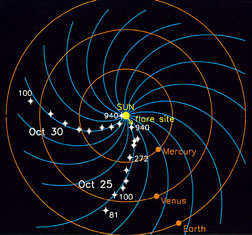
IMF stands for Interplanetary Magnetic Field. It is another name for the Sun's magnetic field. The Sun's magnetic field is enormous and is carried by the solar wind. The solar wind and magnetic field are
...more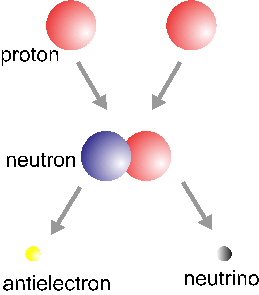
The basic Hydrogen fusion cycle involves four Hydrogen nuclei (protons) and two electrons and yields a Helium nucleus, two neutrinos and six photons. This process occurs in three steps: the first one is
...more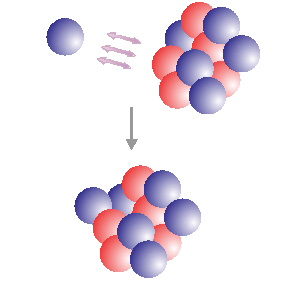
Neutron capture can occur when a neutron approaches a nucleus close enough for nuclear forces to be effective. The neutron is captured and forms a heavier isotope of the capturing element. When the new
...more
A Supernova is a very massive star that explodes at the end of its life cycle. The supernova is the furnace where the heavy elements (heavier than iron) are formed by neutron capture.
...more