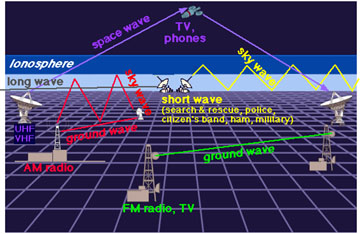
Various types (frequencies) of radio waves are used for communications.
Click on image for full size
Windows to the Universe original artwork.
Radio Waves
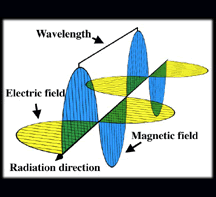
Radio waves are a type of electromagnetic
radiation. A radio wave has a much
longer wavelength than
does visible
light. We use radio waves extensively for communications.
Radio waves have wavelengths as short as a few millimeters (tenths of inches)
and as long as hundreds of kilometers (hundreds of miles). Visible light, for
comparison, has wavelengths in the 400 to 700 nanometer range, about 5,000
times shorter than the shortest wavelength radio waves. Radio waves oscillate
at frequencies between a few kilohertz (kHz or thousands of hertz) and a few
terahertz (THz or 1012 hertz). "Far
infrared" radiation borders radio waves on the
electromagnetic spectrum; far IR is slightly higher energy and shorter wavelength
radiation than radio.
Microwaves, which we use for cooking and for communication, are short wavelength
radio waves with wavelengths between a few and a few hundred millimeters (tenths
of inches to tens of inches).
Various frequencies of radio waves are used for television and FM and AM radio
broadcasts, military communications, mobile phones, ham radio, wireless computer
networks, and numerous other communications applications.
Most radio waves pass freely through Earth's atmosphere. However, some frequencies
can be reflected or absorbed by the charged particles in the ionosphere.
You might also be interested in:
There are many kinds of waves all around us. Everyone knows about waves of water in the ocean. Did you also know that sound travels through the air in waves? Or that light is actually made up of waves
...more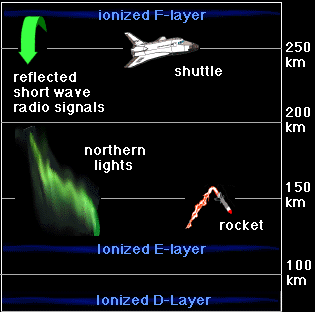
The ionosphere is broken down into the D, E and F regions. The breakdown is based on what wavelength of solar radiation is absorbed in that region most frequently. The D region is the lowest in altitude,
...more
How do scientists measure space weather? Let's take a look! Scientists watch the Sun with special telescopes. Some of the telescopes are on Earth, while others are on satellites. Some of the telescopes
...more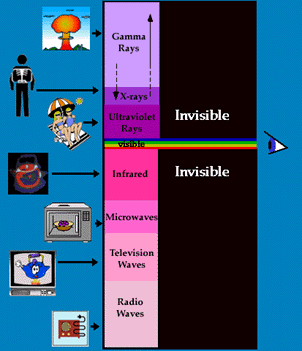
Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation that is very familiar to us. However, there are several other forms of electromagnetic (EM) radiation, such as X-rays, radio waves, and ultraviolet and infrared
...more
You know, of course, that certain conditions in the Earth's atmosphere can cause powerful storms like thunderstorms, blizzards, tornadoes, and hurricanes. The Sun also has an atmosphere, and incredible
...more
Solar flares are essentially huge explosions on the Sun. Flares occur when intense magnetic fields on the Sun become too tangled. Like a rubber band that snaps when it is twisted too far, the tangled magnetic
...more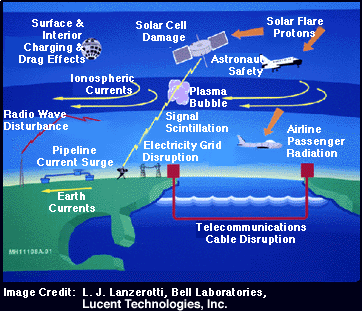
Space weather affects people and society in many ways. Let's take a look at the ways radiation and magnetic disturbances in space can affect us here on Earth. Space weather "storms" can disrupt radio signals.
...more
With just our eyes, we can see many things in the night sky, including stars, planets, meteors, comets, auroras, and the Moon. Have you ever looked up and wished that you could take a closer look at the
...more